Back to selection
GEO Satellite
Telstar-5 (Intelsat Americas 5, Galaxy-25) GEO
succesfull

Inclined
Launch date
24 May 1997
Country

Purpose
Communication
Position
33° East
Manufacturer
Operator
Launch operator
Launch vehicle
Proton K
Expected lifetime
12 Years

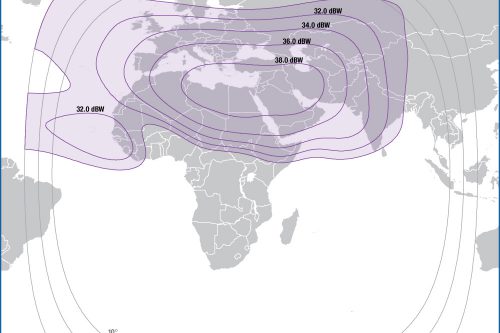
Regions
Asia Pacific Region
Europe Region
Middle East Region
North & Central Africa Region
Under a contract with Loral Skynet Satellite Services, Space Systems/Loral (SS/L) built and launched three new-generation communications satellites, Telstar-5, -6 and -7. Launched in 1997, Telstar-5, was the highest capacity satellite in the U.S. telecommunications industry.
The three spacecraft would serve the USA, southern Canada, Mexico and the Caribbean. Since the satellites were delivered in orbit, SS/L completed responsibility for launch services and risk management.
The hybrid Telstar-5 and Telstar-6 are each outfitted with 24 C-band and 28 Ku-band transponders and generate a total of 3,200W of on-board transmitter power. Telstar-7 carries 24 C-band and 24 Ku-band transponders but use more powerful components to provide identical rf power.
Lightweight composite materials and highly efficient techniques for dissipating thermal energy and for generating and storing electricity allow for a substantial increase in the spacecraft abilities, with almost no increase in size and weight.
The three geostationary Telstar spacecraft are based on SS/L’s three-axis, body-stabilized 1300 platform. SS/L’s 1300 buses are designed to achieve long useful orbital life through use of a bi-propulsion system and a momentum-bias system for excellent station-keeping and orbital stability. Solar arrays and nickel-hydrogen batteries provide uninterrupted electrical power.
In 2003 Loral sold Telstar-5, -6 and -7 to Intelsat, who operated the satellites as Intelsat Americas 5, -6 and -7.In February 2007, satellite operator Intelsat changed the name of the Intelsat Americas satellites to Galaxy-25, -26 and -27.
Telstar-6 suffered a control processor failure in 2001, but no service loss occurred. Intelsat Americas 7’s electrical-distribution system suddenly failed on 28 November 2004. Contact was regained a few days later, with 22 transponders returning to operation. Galaxy-26 reached its operational end of life on 7 June 2014, when the final command was sent. Galaxy-27 was retired in 2016 and was moved into a graveyard orbit above the geostationary belt.
Telstar-5 was successfully launched on May 24th, 1997 on a Proton K rocket booster operated by launch operator ILS from the Baikonur Cosmodrome launch site in Kazachstan.
GEO Satellite
Telstar-5 (Intelsat Americas 5, Galaxy-25)
succesfull