
Back to selection

Supplier
Guodian Gaoke
Guodian Gaoke
Building 1, Yongyou Industrial Park West Area
68 Beiqing Rd.
Haidian District
Beijing
China
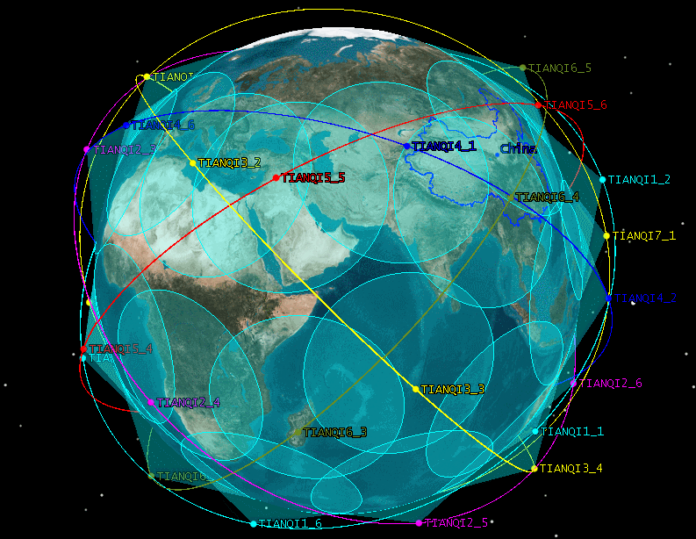
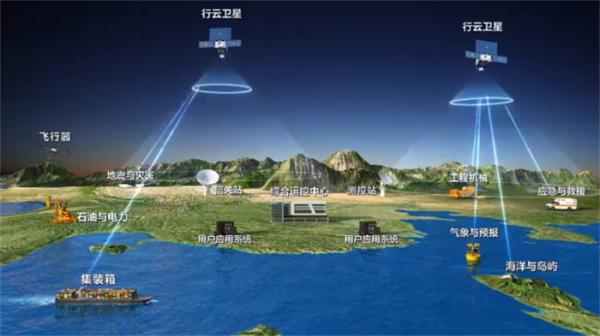
Guodian Gaoke (Guodian Gaokeji) is a Chinese private commercial space company and leading provider of domestic satellite IoT. The company is building a Low Earth Orbit IoT narrowband constellation, Tianqi, composed of 38 LEO satellites, which aims at enhancing connectivity and efficiency through smart, connected devices.
The company, founded in 2015, has established a satellite application joint laboratory with the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications as well as with Beihang University and plans to complete the entire constellation by the end of 2022.
Guodian Gaoke is based in Bejing, currently has 16 satellites in orbit and completed the first phase of the constellation deployment in July 2021. The satellites enable a fly-over every 1.5 hours and consequently an update of a given sensor’s status. This frequency is deemed sufficient for most applications of industry verticals targeted by the Chinese company.
Company History
The company was established in June 2015 by Lu Qiang (CEO) and Zhang Jinwu. Qiang is specialized in IoT and is presently the director general of the China Satellite Internet of Things Industry Alliance. Jinwu holds a master’s degree at the China Astronaut Research and Training Center and an MBA at the China Europe International Business School.
In October 2018 Guodian Gaoke launched its first satellite, Tianqi-01, as a co-passenger to the Chinese-French Oceanography Satellite, CFOSAT, on a CZ-2C rocket operated by CGWIC from China.
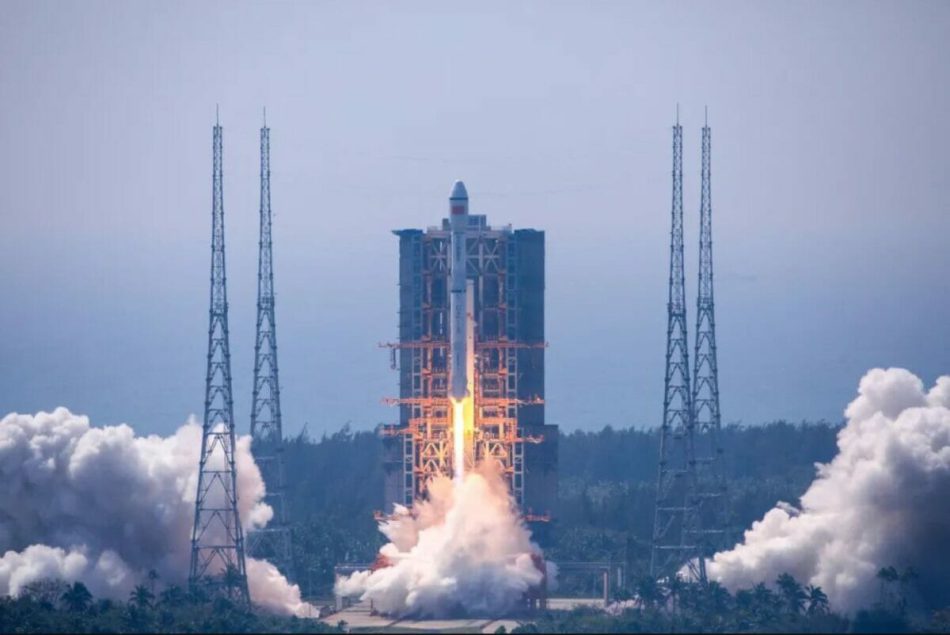
On December 21st, 2020 CGWIC launched Guodian Gaoke’s Tianqi-08 (Xingzuo-08) Nano-satellite, as part of a commercial Rideshare payload of five satellites, into orbit on their Long March 8 first mission, debuting an expendable booster intended to eventually be outfitted for recovery and reuse. The Long March 8 rocket took off from the Wenchang satellite launch center on Hainan Island, China’s newest spaceport.
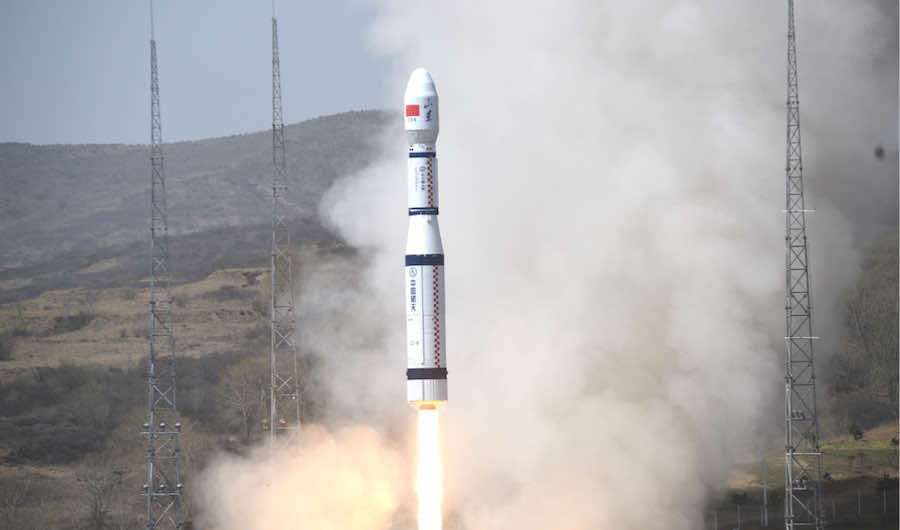


On April 27th, 2021 launch provider CGWIC orbited nine Nano-satellites for Guardian Gaoke with a Long March 6 rocket on a rideshare mission.
On February 26th, 2022 a Long March 8 launcher, operated by CGWIC, orbited the Tianqi-19 Nano-satellite. The spacecraft was manufactured by Shandong Institute of Aerospace Electronics Technology for Guodian Gaoke and its Tianqi low-Earth orbit narrow-band Internet of Things constellation.
On December 9th, 2022 the company launched its Tanqi-7 Nano-satellite using the Jielong-3 rocket that made its maiden flight launching from a floating platform from the Yellow Sea. Jielong-03 or Smart Dragon-3 or SD-3, is operated by China Rocket, a spinoff of state-owned CALT.
On January 9th, 2023 the company launched Tianqi-13 LEO satellite on a Ceres-1 rocket launcher operated by launch operator Galactic Energy from Jiuquan spaceport in the Gobi Desert in northwest China. Tianqi-13 was among five satellites that were sent into SSO; Tianmu-1 01 and -02, both meteorological satellites, and a ‘Science and Technology-1’ remote sensing satellite and a small satellite for science outreach named for Nantong Middle School.
On December 19th, 2024, the company made the fourth sea-based launch mission of its Ceres-1carrier rocket. The satellites were built by satellite operator Guodian Gaoke, for its Tianqi network.
| Satellite(s) | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Provider |
| Tanqi-01 | Oct 29th, 2018 | CZ-2C | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-02 | Aug 17th, 2019 | Jielong-1 | CASC, China |
| Tanqi-03 | June 5th, 2019 | CZ-11H | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-4A & -4B | Dec 7th, 2019 | Kuaizhou-1 | CASIC, China |
| Tanqi-05 | Jan 15th, 2020 | CZ-2D | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-06 | Oct 26th, 2020 | CZ-2C | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-07 | Dec 9th, 2022 | Jielong-3 | China Rocket, China |
| Tanqi-08 | Dec 21st, 2020 | LM-8 | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-09 | Apr 27th, 2021 | CZ-6 | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-10 | July 25th, 2020 | CZ-4B | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-11 | Nov 7th, 2020 | Ceres 1 | Galactic Energy, China |
| Tanqi-12 | May 6th, 2021 | CZ-2C | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-14 | June 18th, 2021 | CZ-2C | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-15 | July 19th, 2021 | CZ-2C | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-19 | Feb 26th, 2022 | LM-8 | CGWIC, China |
| Tanqi-13 | Jan 9th, 2023 | Ceres 1 | Galactic Energy, China |
| Tanqi-21 to -24 | Sep 5th, 2023 | Ceres 1 | Galactic Energy, China |
| Tanqi-25 to -28 | May 29th, 2024 | Ceres 1 | Galactic Energy, China |
| Tanqi-29 to -32 | Sep 20th, 2024 | Kuaizhou-1A | CASC, China |
| Tanqi-33 to -36 | Dec 19th, 2024 | Ceres 1 | Galactic Energy, China |
All trademarks, logos and images mentioned and showed on this page are property of their respective owners.
Resources
www.guodiangaoke.com
www.dongfanghour.com edition September 15th, 2021
www.ventureradar.com
www.newspace.im
www.spacenews,com edition December 22nd, 2020
www.spaceflightnow.com edition December 26th, 2020
www.nanosats.eu
www.space.skyrocket.de
www.spaceflightnow.com edition April 30th, 2021
www.spacenews.com edition February 27th, 2022
www.cbinsights.com
www.space.com edition August 7th, 2022
www.space.com edition January 9th, 2023

Supplier
Guodian Gaoke
Guodian Gaoke
Building 1, Yongyou Industrial Park West Area
68 Beiqing Rd.
Haidian District
Beijing
China
Smallsats launched by Guodian Gaoke
| Smallsat | Country | |||
| TIANQI-41 (TQ-41)LEO | Ceres-1S Y7 / ‘Wang-Hai-Chao’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-40 (TQ-40)LEO | Ceres-1S Y7 / ‘Wang-Hai-Chao’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-39 (TQ-39)LEO | Ceres-1S Y7 / ‘Wang-Hai-Chao’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-38 (TQ-38)LEO | Ceres-1S Y7 / ‘Wang-Hai-Chao’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-37 (TQ-37)LEO | Ceres-1S Y7 / ‘Wang-Hai-Chao’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-32 (TQ-32)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y31 / TIANQI-29 -32 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-31 (TQ-31)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y31 / TIANQI-29 -32 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-30 (TQ-30)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y31 / TIANQI-29 -32 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-29 (TQ-29)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y31 / TIANQI-29 -32 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-12LEO | CASC CZ-2C Y47 / Yaogan 30-08A – 08C | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-14LEO | CASC CZ-2C Y48 / Yaogan 30-09A – 09C | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-15 (TQ-15)LEO | CASC CZ-2C Y49 / Yaogan 30-10A – 10C | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-1 (TQ-1)LEO | Ceres-1 Y1 / ‘I Believe I Can Fly’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-24 (TQ-24)LEO | Ceres-1S Y1 / ‘The-Little-Mermaid’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-23 (TQ-23)LEO | Ceres-1S Y1 / ‘The-Little-Mermaid’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-22 (TQ-22)LEO | Ceres-1S Y1 / ‘The-Little-Mermaid’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-21 (TQ-21)LEO | Ceres-1S Y1 / ‘The-Little-Mermaid’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-10 (TQ-10)LEO | CASC CZ-4B Y45 / Ziyuan 3-03 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-28 (TQ-28)LEO | Ceres-1S Y2 / ‘Beautiful-World’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-27 (TQ-27)LEO | Ceres-1S Y2 / ‘Beautiful-World’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-26 (TQ-26)LEO | Ceres-1S Y2 / ‘Beautiful-World’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-25 (TQ-25)LEO | Ceres-1S Y2 / ‘Beautiful-World’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-36 (TQ-36)LEO | Ceres-1S Y4 / ‘Loong’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-35 (TQ-35)LEO | Ceres-1S Y4 / ‘Loong’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-34 (TQ-34, Baoding Lianchi)LEO | Ceres-1S Y4 / ‘Loong’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-33 (TQ-33, Shantou Shuzi-1)LEO | Ceres-1S Y4 / ‘Loong’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-20 (TQ-20)LEO | Ceres-1S Y5 / ‘Huai-Xu-Fei-Tang’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-18 (TQ-8)LEO | Ceres-1S Y5 / ‘Huai-Xu-Fei-Tang’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-17 (TQ-16)LEO | Ceres-1S Y5 / ‘Huai-Xu-Fei-Tang’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-16 (TQ-6)LEO | Ceres-1S Y5 / ‘Huai-Xu-Fei-Tang’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-8 (TQ-8, Ping’an-1)LEO | CASC CZ-8 Y1 / XJY-7 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-13 (TQ-13)LEO | Ceres-1 Y5 / ‘Give-Me-Five’ | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-19 (TQ-19)LEO | CASC CZ-8 Y2 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-4B (TQ-4B)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y12 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-4A (TQ-4A)LEO | Kuaizhou-1A Y12 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-5 (TQ-5)LEO | CASC CZ-2D Y58 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-7 (TQ-7)LEO | Jielong-3 Y1 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-2 (TQ-2)LEO | Jielong-1 Y1 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-3 (TQ-3, Tao Xingzhi)LEO | CASC CZ-11H Y1 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |
| TIANQI-9 (TQ-9)LEO | CASC CZ-6 Y5 | Guodian Gaoke |  | loT |