GHGSat LEO satellite constellation

| Position: | LEO |
| Operator: | GHGSat |
| Launch operators: | Arianespace |
| Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) | |
| SpaceX | |
| Launch vehicles: | Falcon 9 |
| PSLV | |
| Vega | |
| Launch date: | |
| Expected lifetime: | 10 Years |
The GHGSat LEO satellite constellation is operated by GHGSat (Greenhouse Gas Satellite) based in Montreal, Canada. The company is currently operating three satellites in LEO orbit and plans to build a constellation of 10 satellites, providing actionable greenhouse gas emissions data and insights to businesses, governments, financial markets and regulators worldwide.
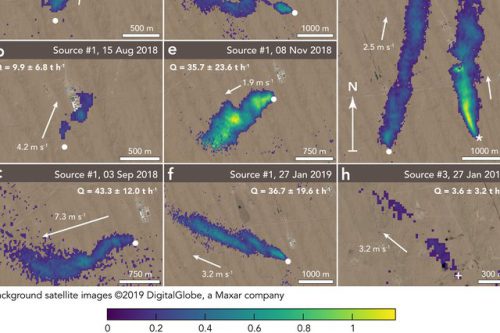
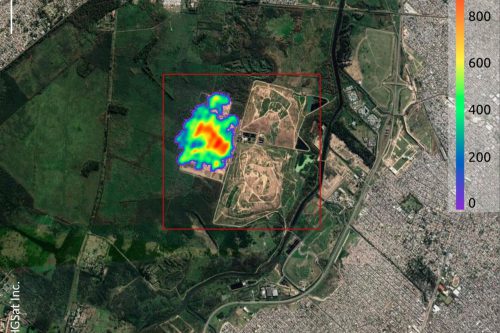
On June 21st, 2016 the companies first satellite, the Demonstration satellite GHGSat-D (Claire), was launched on the PSLV-C34 Mission with a PSLV launch vehicle operated by ISRO from India. GHGSat-D was the world’s first high-resolution satellite capable of measuring greenhouse gas (CO2 & CH4) emissions from any industrial facility in the world. The company is using this unique satellite and its patented technology to provide greenhouse gas emissions monitoring data and services globally, with better accuracy and at a fraction of the cost of comparable alternatives.
On September 2nd, 2020 the launch operator Arianespace orbited the GHGSat-C1 (Iris) satellite using their Vega rocket from the Kourou Spaceport in French Guiana.
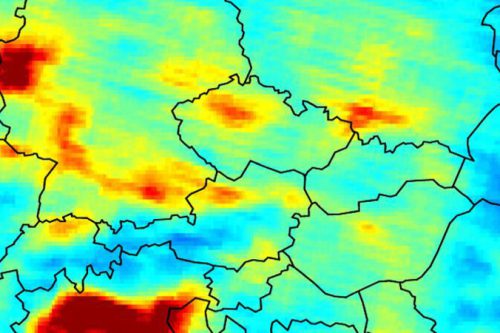
On October 21st, 2020 GHGSat unveiled a free map, Pulse, showing average weekly methane concentrations around the world at a resolution of approximately two km per pixel. The map showed changes in methane concentrations measured in parts per million or parts per billion for each pixel during the year, to raise awareness and stimulate climate change discussion.
On January 24th, 2021 launch operator SpaceX launched the GHGSat-C2 (Hugo) satellite on the Rideshare Transporter-1 mission on a Falcon 9 rocket.
In December 2021 the company signed a contract with launch operator SpaceX for the launch of the next batch of satellites, GHGSat-C3, – C4 and -C5. The three satellites, each weighing 15kgs and similar to the GHGSat-C1 and -C2 satellites, are being built by the University of Toronto’s Space Flight Laboratory (SFL) with gas detection payloads provided by ABB.
| Satellite | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| GHGSat-D (Claire) | PSLV-C34 | June 21st, 2016 | PSLV | ISRO India |
| GHGSat-C1 (Iris) | VV16 | Sept 2nd, 2020 | Vega | Arianespace FG |
| GHGSat-C2 (Hugo) | Transporter-1 | Jan 24th, 2021 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C3 (Luca) | Transporter-5 | May 25th, 2022 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C4 (Penny) | Transporter-5 | May 25th, 2022 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C5 (Diako) | Transporter-5 | May 25th, 2022 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C6 (May-Lin) | Transporter-7 | Apr 15th, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C7 (Gaspard) | Transporter-7 | Apr 15th, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| GHGSat-C8 (Océane) | Transporter-7 | Apr 15th, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |