Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)

| Position: | MEO |
| Manufacturer: | Mitsubishi Electric |
| Operator: | JAXA |
| Launch operator: | MHI Launch Services |
| Launch vehicle: | H-IIA |
| Launch date: | |
| Expected lifetime: |
Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS)
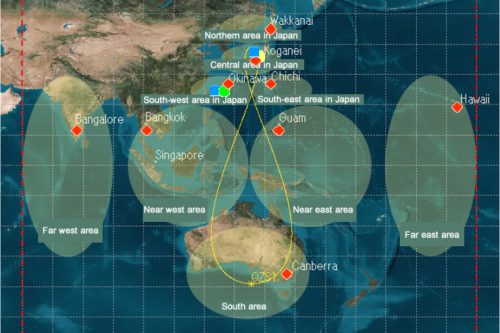
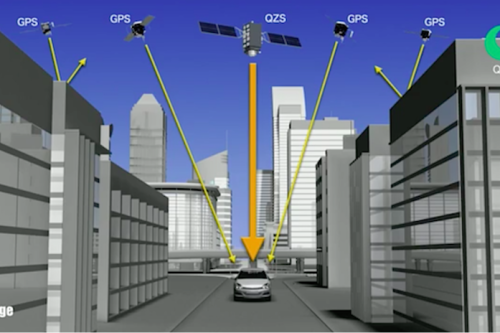
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), also known as Michibiki, is a regional time transfer system and satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government. Its primary objective is to enhance the functionality of the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) in the Asia-Pacific and Oceania regions, with a specific focus on Japan. QZSS aims to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in this region, while remaining compatible with GPS.
As of January 12th, 2018, QZSS services with four satellites became available on a trial basis, and they were officially launched on November 1st, 2018. Furthermore, there are plans to develop a satellite navigation system independent of GPS by 2023, utilizing a total of seven satellites operated by Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
QZSS comprises of one geostationary satellite and three satellites in Tundra-type highly inclined, slightly elliptical, geosynchronous orbits. These orbits are positioned 120° apart from each other. Unlike geostationary satellites, the QZSS satellites are not fixed in a specific location in the sky due to their inclination. Instead, they follow asymmetrical figure-8 patterns (analemmas) on the ground, ensuring that at least one satellite is almost directly overhead (elevation of 60° or more) over Japan at all times. The satellites have been launched by launch operator MHI Launch Service.
History
In 2002, the Japanese government sanctioned the development of QZSS as a regional time transfer system comprising three satellites. Its purpose was to augment the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) and provide coverage within Japan. Advanced Space Business Corporation (ASBC) and a consortium consisting of Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, and GNSS Technologies, Inc. were awarded the contract for concept development. However, ASBC faced financial difficulties and ceased operations in 2007. The project was then transferred to the Satellite Positioning Research and Application Center (SPAC), which is jointly owned by four Japanese government departments: the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
The first QZSS satellite, named “Michibiki,” was launched on September 11th, 2010. The system was expected to achieve full operational status by 2013. In March 2013, the Cabinet Office of Japan announced the expansion of QZSS from three satellites to four. Mitsubishi Electric was awarded a 526 million USD-contract for the construction of three additional satellites, with the aim of launching them before the end of 2017. The third satellite was successfully launched into orbit on August 19th, 2017, followed by the launch of the fourth satellite on October 10th, 2017. On November 1st, 2018, the four-satellite system reached its operational status and was officially declared as such.
| Satellite (Nickname) | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| QZS-1 (Michibiki-1) | Sep 11th, 2010 | H-IIA F18 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-2 (Michibiki-2) | June 1st, 2017 | H-IIA F34 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-3 (Michibiki-3) | Aug 19th, 2017 | H-IIA F35 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-4 (Michibiki-4) | Oct 10th, 2017 | H-IIA F36 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-1R (Michibiki-1R) | Oct 26th, 2021 | H-IIA F44 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-5 | 2024 | H3 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-6 | 2024 | H3 | MHI Launch Service JP | |
| QZS-7 | 2025 | H3 | MHI Launch Service JP |