UnseenLabs BRO LEO satellite constellation

| Position: | LEO |
| Manufacturer: | GOMSpace |
| Operator: | Unseenlabs |
| Launch operators: | Arianespace |
| Rocket Lab | |
| SpaceX | |
| Launch vehicles: | Electron |
| Falcon 9 | |
| Vega | |
| Launch date: | |
| Expected lifetime: | 10 Years |
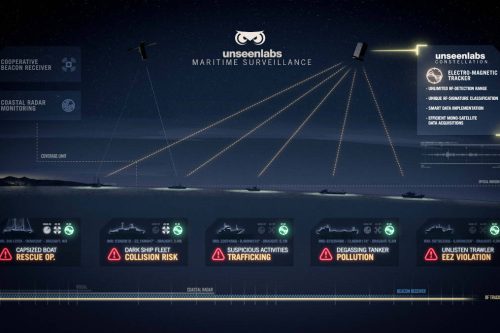
UnseenLabs BRO (Breizh Reconnaissance Orbiter) LEO satellite constellation is being created by French space start-up company Unseenlabs. The constellation is built for maritime surveillance.
The company is leading in radio Frequency sign al processing thru their satellites and is providing services to Maritime-, and Shipping companies, Security companies and Governments for environmental protection. Almost 90% of goods are transported by sea and oceans, new shipping routes are opened and piracy and illegal vessels are ever present. When a vessel is hi-jacked it can vanish from the surveillance screens if its embedded beacon (Automatic Identification System, AIS) is cut-off. With UnseenLabs’ innovative electromagnetic technology a vessel can be tracked any time worldwide.
The BRO-1 LEO satellite was developed by the company, and is a spectrum monitoring and electromagnetic intelligence service (SIGINT) for maritime and aerial traffic surveillance. The satellite is a 6U CubeSat and was built by GOMSpace featuring the company’s-built spectrum monitoring payload. This was the first step towards a future constellation using advanced spectrum monitoring dedicated to a disruptive maritime surveillance service.
The BRO-2 and BRO-3 satellites were launched on November 20th 2020 on an Electron KS launcher operated by Rocket Lab.
Their fourth satellite, BRO-4, was orbited on a Vega launcher, operated by launch provider Arianespace, on August 17th, 2021. The satellite was orbited into a sun-synchronous orbit (SSO) at an altitude of (approximately) 551 km.
BRO-5 satellite was orbited on the Spacex’ Transporter-3 Rideshare Mission on Jan 13th, 2022 using a Falcon 9 rocket.
BRO-6 was launched on Rocket Lab’s Electron launcher from Pad A at Launch Complex 1 on New Zealand’s Mahia Peninsula. The ‘There And Back Again’ mission was Rocket Lab’s 26th Electron launch deploying 34 satellites to a sun synchronous orbit for a variety of customers including Alba Orbital, Astrix Astronautics, Aurora Propulsion Technologies, E-Space, Spaceflight Inc, and Unseenlabs. The mission brought the total number of satellites launched by Electron to 146 and was also a recovery mission where, for the first time, Rocket Lab caught Electron’s first stage as it returned from space under parachutes using a helicopter. The successful catch brings Electron one step closer to being the first reusable orbital small sat launcher.
|
Satellite
|
Mission
|
Launch Date
|
Launcher
|
Launch Operator
|
|
BRO-1
|
‘Look-Ma,-No-Hands’
|
Aug 19th, 2019
|
Electron
|
Rocket Lab NZ
|
|
BRO-2
|
‘Return-To-Sender’
|
Nov 20th, 2020
|
Electron
|
Rocket Lab NZ
|
|
BRO-3
|
‘Return-To-Sender’
|
Nov 20th, 2020
|
Electron
|
Rocket Lab NZ
|
|
BRO-4
|
VV19
|
Aug 17th, 2021
|
Vega
|
Arianespace FG
|
|
BRO-5
|
Transporter-3
|
Jan 13th, 2022
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|
|
BRO-6
|
‘There-And-Back-Again’
|
May 2nd, 2022
|
Electron
|
Rocket Lab NZ
|
|
BRO-7
|
Transporter-4
|
April 1st, 2022
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|
|
BRO-8
|
Transporter-6
|
Jan 3rd, 2023
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|
|
BRO-9
|
Transporter-7
|
Apr 15th, 2023
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|
|
BRO-10
|
Transporter-9
|
Nov 11th, 2023
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|
|
BRO-11
|
Transporter-9
|
Nov 11th, 2023
|
Falcon 9
|
SpaceX USA
|