
Back to selection

Supplier
Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services)
Space Norway
Snarøyveien 30
M3A 1360 Fornebu
Norway
Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) is Northern Europe’s leading satellite operator, providing secure and reliable connectivity to governments, public and defense sectors, maritime, land-based industries, and broadcasters. The company’s advanced infrastructure supports clients across Europe, the Arctic, the Middle-East, and Africa.
Telenor Satellite Services was the satellite operator of Norway operating as subsidiary of the Telenor Group. The company was headquartered in Fornebu in Bærum, close to Oslo, and was one of the world’s largest mobile telecommunications companies with operations in Scandinavia, Eastern Europe and Asia. Telenor had operations in 29 countries and operates three satellites in orbit (THOR-5, THOR-6 and THOR-7) and owns seven Ku-band transponders on the Spot 1 and Spot 2 payload for high-powered coverage throughout Europe and the Middle-East. The Group had 182 million customers and annual sales of around 12 billion USD (2019).
In November 2023 the Telenor Group sold its Telenor Satellite subsidiary to Space Norway for 220 million USD. Both entities are owned by the Norwegian government. Telenor is Norway’s majority state-owned telecommunications company, and Space Norway is owned by the Norwegian Ministry of Trade, Industry and Fisheries and is a key part of the country’s activities in the space sector. The sale will establish a major Norwegian satellite operator maintaining the control over satellites strengthening Norway as a space nation.


Company History
Telenor was established in 1855 as a state-operated monopoly, named Telegrafverket as a provider of telegraph services. The first ideas for a telegraph were launched within the Royal Norwegian Navy in 1848, but by 1852 the plans were public and the Parliament of Norway decided on a plan for constructing the telegraph throughout the country. Televerket began by building from Christiania (now Oslo) to Sweden as well as between Christiania and Drammen. In 1857 the telegraph had reached Bergen (west coast) via Sørlandet (south coast) and in 1871 it had reached Kirkenes (north coast). Cable connections were opened to Denmark in 1867 and to the UK in 1869. The telegraph was most important for the merchant marine that now could use the electric telegraph to instantly communicate between different locations, and get a whole new advantage within logistics.
The corporation changed its name to Televerket in 1969. In 1994, the then Norwegian Telecom was established as a public corporation. The authorities wanted to deregulate the telecom sector in Norway, and sector by sector was deregulated between 1994 to 1998. An attempt to merge Telenor with its counterpart in Sweden, Telia, failed in 1999, while both still were owned by their respective governments.
On December 4th, 2000 the company was partially privatized and listed on Oslo Stock Exchange and NASDAQ. The privatization gave the company NOK 15,6 billion in new capitals, the Government of Norway owning almost 78% of the company after the privatization. As of 2014, the Norwegian government holds 54% of the Telenor shares directly and another 4.7% through the Pension Fund.
In the second half of the 90’s, Telenor became involved in mobile operations in a number of countries: Russia (1994), Bangladesh, Greece, Ireland, Germany and Austria (1997), Ukraine (1998), Malaysia (1999), Denmark and Thailand (2000), Hungary (2002), Montenegro (2004), Pakistan (2004), Slovakia, Czech Republic, Serbia (2006), Myanmar (2014). Operations in Greece, Ireland and Germany were sold in 1999/2000 and profits were re-invested in the emerging markets.
In October 2005 Telenor acquired Vodafone Sweden, changing the name to Telenor in April 2006. On 31 July 2006, Telenor acquired 100% share of Serbian mobile operator Mobi 63 for 1.5 billion euro.
October 25th 2006, the Telenor Group agreed with France-based private equity investment group Apax Partners, to sell Telenor Satellite Services (TSS) to funds managed by Apax Partners for a cash consideration of 400 million USD (NOK 2,640 million). Since 2002 Telenor Group defined TSS as non-core business. Apax had originally purchased France Telecom Mobile Satellite Communications (FTMSC) , the satcoms arm of France Telecom, for 60 million euro in July 2006. FTMSC was renamed in Vizada in 2007. The acquisition of Telenor Satellite Services resulted in the formation of Vizada Networks.
In December 2011 Apax sold the Vizada group to Aerospace company EADS (Airbus Defense & Space) for approximately 1 billion USD to form its Astrium Services businessunit.
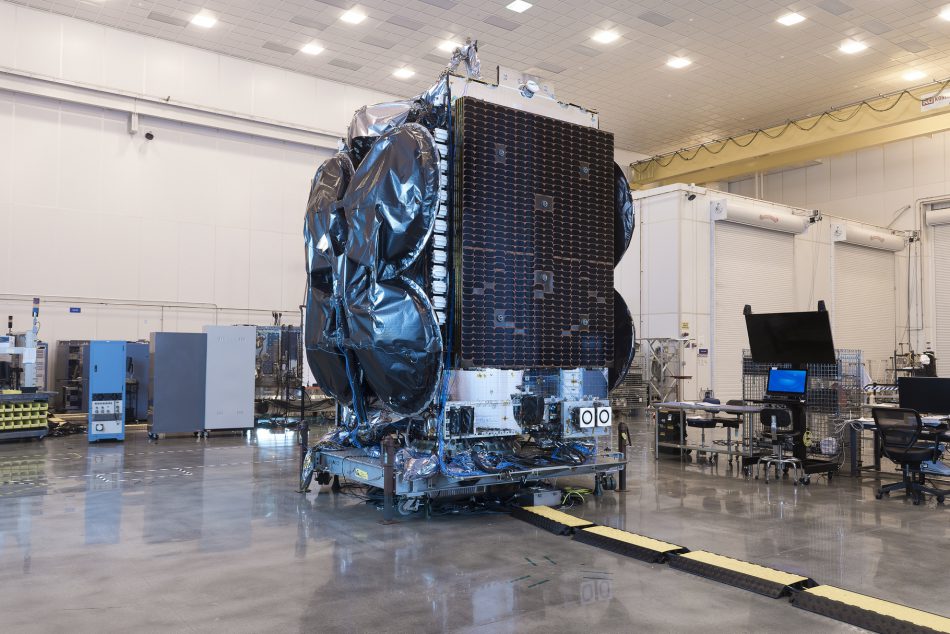
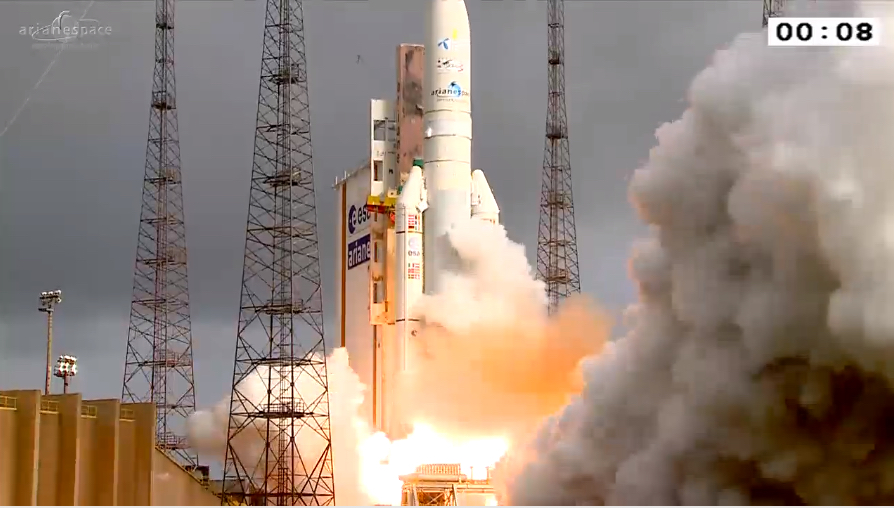
On April 27th 2015 the THOR-7 satellite, manufactured by Space Systems/Loral (SS/L) was successfully orbited by launch operator Arianespace. The satellite was lifted in a dual launch with the SICRAL-2 spacecraft for Telespazia, on behalf of the Italian Ministry of Defense.


In 2016 Apax Partners re-acquired the commercial Satellite Communications Business of Airbus and rebranded as Marlink. All maritime and enterprise satcom activities was grouped under this brand.
Also in 2016 Telenor Satellite Broadcasting changed its name to Telenor Satellite. In that same year Telenor Group became one of the world’s largest mobile operators, with over 19.000 employees, 214 million mobile subscriptions and a record revenue of 131 billion NOK.
In April 2018 Telenor signed a multi-transponder agreement with satellite operator Intelsat to support growth of leading Direct-to-Home (DTH) platform in Central and Eastern Europe. The agreement will provide Intelsat with satellite capacity for its broadcast customers on the THOR-5 and THOR-7 satellites.
In November 2023, the Telenor Group divested its Telenor Satellite subsidiary to Space Norway for a total of 220 million USD. Notably, both organizations are under the ownership of the Norwegian government. Telenor, as the majority state-owned telecommunications company in Norway, decided to transfer its satellite subsidiary to Space Norway, an entity owned by the Norwegian Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Fisheries. Space Norway holds strategic significance in the nation’s space sector initiatives. This transaction is poised to create a significant Norwegian satellite operator, consolidating control over satellites and contributing to the enhancement of Norway’s standing as a prominent player in the realm of space activities.
On February 10th, 2025 Space Norway ordered THOR-8 (GEO) satellite with Thales Alenia Space. TAS will be responsible for the design, manufacture, testing, and delivery of the satellite, which will have three dedicated payloads on the Ku- and Ka-bands. THOR-8 will be launched in 2027 and will have an in-orbit service life of over 15 years.
All trademarks, logos and images mentioned and showed on this page are property of their respective owners.
Resources
www.telenorsat.com
www.telenor.com
www.satbeams.com
www.wikipedia.org
www.telenorkulturarv.no
www.zippia.com
www.marinelink.com edition October 26th 2006
www.globalnewswire.com edition October 26th 2006
www.thedigitalship.com
www.businesswire.com edition September 6th 2007
www.apax.fr
www.bloomberg.com edition December 21st 2015
www.smartmaritimenetwork.com edition March 20th 2019
www.marlink.com
www.satellitetoday.com edition November 20th, 2023
www.spacenorway.com
www.satellitetoday.com edition February 10th, 2025
www.satellitetoday.com edition April 2nd, 2025

Supplier
Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services)
Space Norway
Snarøyveien 30
M3A 1360 Fornebu
Norway
Satellite fleet by Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services)
| Satellite | Country | |||
| ASBM-1 (GX-10A, EPS-R 1)HEO | 65° North | Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) |  | Communication |
| ASBM-2 (GX-10B, EPS-R 2)HEO | 65° North | Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) |  | Communication |
| Intelsat 10-02 (THOR 10-02) (ext. lifespan with MEV-2)GEO | 1° West | Intelsat |  | Communication |
| THOR 3 (THOR III)GEO | 4° West | Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) |  | Communication |
| THOR 5 (THOR-2R)GEO | 1° West | Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) |  | Communication |
| THOR 6 (Intelsat-1W)GEO | 1° West | Intelsat |  | Communication |
| THOR 7GEO | 1° West | Space Norway (former Telenor Satellite Services) |  | Communication |