Back to selection
GEO Satellite
Inmarsat-5 F1 (Inmarsat GX1, IS IOR) GEO
succesfull

Active
Launch date
8 December 2013
Dedicated Mission
Country

Purpose
Communication
Position
63° East
Manufacturer
Operator
Expected lifetime
15+ Years

Regions
Asia Pacific Region
Europe Region
Middle East Region
North & Central Africa Region
Oceania Region
Russia & CIS Region
South Africa Region
Inmarsat-5 F1 satellite is operated by satellite operator Inmarsat from the UK. The satellite is one of the next-generation Inmarsat fleet satellites aimed to boost connectivity speeds for users on-the-move in airplanes, on boats and on land.
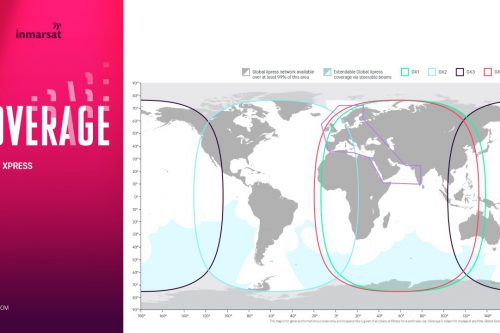
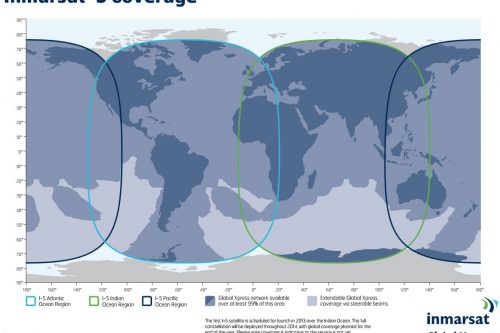
With 89 fixed and steerable Ka-band beams, the Global Xpress satellites represent new territory for Inmarsat, which used a different radio band on earlier satellites. Switching from L-band to Ka-band improves downlink communications speeds to 50Mbps, with up to 5Mbps on the uplink side. And users can link up with the Global Xpress satellites with smaller terminals. Inmarsat-5 F1 will take up operations at 63° East longitude covering the Indian Ocean region.
In August 2010 satellite operator Inmarsat ordered three Ka-band Inmarsat-5 satellites from Boeing to deliver faster broadband to its commercial and government customers by end-2014. In October 2013, Inmarsat ordered a fourth satellite as a spare.
The fixed-price contract with options, valued at 1 billion USD, calls for three high-powered BSS-702HP commercial spacecraft that will operate in geosynchronous orbit with flexible global coverage.
Each Inmarsat-5 satellite will carry 89 Ka-band beams that will operate in geosynchronous orbit with flexible global coverage. The satellites are designed to generate approximately 15kW of power at the start of service and approximately 13.8kW at the end of their 15-year design life. To generate such high power, each spacecraft’s two solar wings employ five panels each of ultra-triple junction gallium arsenide solar cells. The BSS-702HP carries the xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS) for all on-orbit maneuvering. When operational, the Inmarsat-5 satellites will provide Inmarsat with a comprehensive range of global mobile satellite services, including mobile broadband communications for deep-sea vessels, in-flight connectivity for airline passengers and streaming high-resolution video, voice and data.
The Boeing satellites will provide Inmarsat with the ability to adapt to shifting subscriber usage patterns of high data rates, specialized applications and evolving demographics over a projected 15-year lifetime. In a separate arrangement, Boeing has also entered into a distribution partnership with Inmarsat to provide L- and Ka-band capacity to key users within the U.S. government.
The Inmarsat-5 spacecraft are compatible with the Arianespace’ Ariane 5, Sea Launch Zenit-3SL, ILS’ Proton and ULA’s Atlas launch vehicles. Launch services were procured by Inmarsat.
Intelsat-5 F1 was successfully launched on December 8th, 2013, on a Proton M rocket booster, operated by launch operator ILS, from the Baikonour Cosmodrome in Kazachstan.
GEO Satellite
Inmarsat-5 F1 (Inmarsat GX1, IS IOR)
succesfull