
Back to selection

Supplier
EUMETSAT
EUMETSAT
Eumetsat Allee 1
D-64295 Darmstadt
Germany
The European Organization for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT) is an inter-governmental operational organization that was formed in 1986 and created through an international convention agreed by a current total of 30 European Member States. Member countries have full access to data and services and are represented in the supreme decision-making body of the organization, the Council. The company is headquartered in Darmstadt in Germany.
EUMETSAT is not part of the EU, but became a signatory to the International Charter on Space and Major Disasters in 2012, providing the global charitable use of its space assets. Their main objective is to establish, maintain and exploit European systems of operational meteorological satellites. The company’s activities contribute to a global meteorological satellite observing system coordinated with other spacefaring countries.
EUMETSAT has been monitoring the weather and climate from space since the late 70’s, using the Meteosat (GEO) and MetOp (LEO) weather satellites for weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
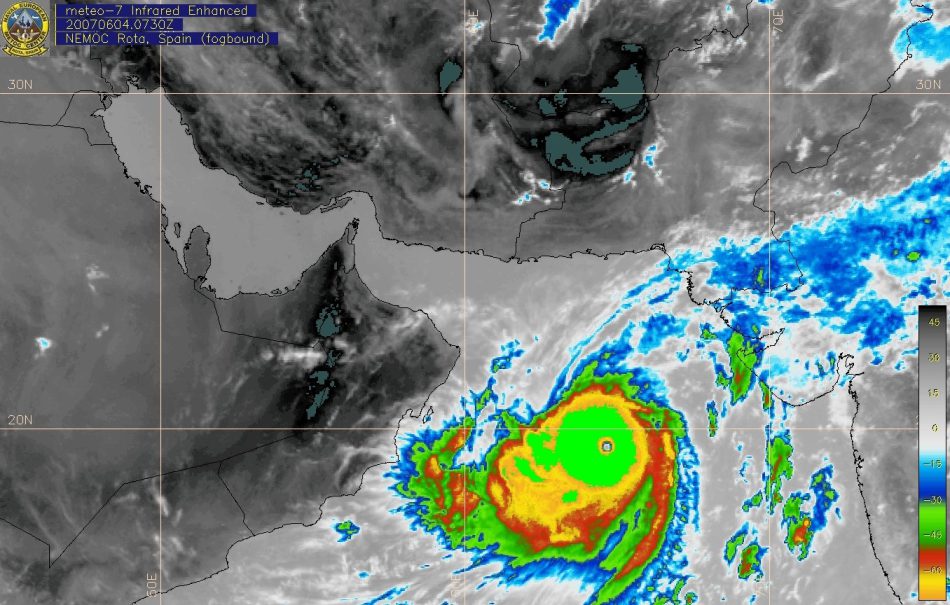
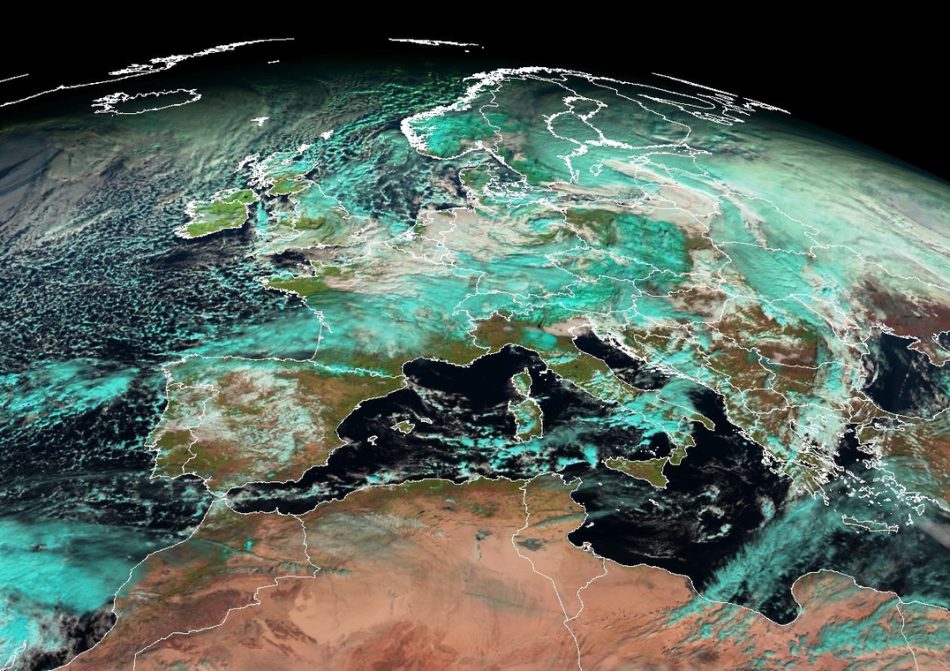
The company is also operating the Copernicus Sentinel-3 and Sentinel-6 satellites and will also operate and deliver products from the Sentinel-4 and Sentinel-5 instruments onboard Meteosat Gen3 and MetOp Gen2 satellites, respectively.
The Jason-series of LEO satellites are providing global sea surface height observations for climate monitoring and ocean and seasonal forecasts. The Jason-3 satellite is the result of an international partnership between EUMETSAT, CNES from France, NOAA and NASA from USA and the European Union, which funds European contributions to Jason-3 operations as part of its Copernicus program. The satellite was launched on January 17th, 2018 on a Falcon 9 rocket operated by SpaceX.
EUMETSAT has established cooperation with operators of Earth observation satellites from Europe and China, India, Japan, South Korea and the USA. The cooperation with Russia was suspended in March 2022 due to Russia’s invasion in the Ukraine.
Meteosat (GEO) weather satellites
EUMETSAT Meteosat weather satellites have been providing data for climate monitoring over Europe and Africa since 1978, building up in the process one of the longest time-series of climate data collected by satellites in the world.
The first Meteosat-1 satellite was launched in November 1977 on a Delta rocket operated by Boeing from the USA. In the following years ESA launched seven more Meteosat satellites that are all inactive. The company currently operates four active GEO weather satellites, Meteosat-9, -10, -11 and -12.
The Meteosat satellites are in geostationary orbit 36,000km above the Earth. They provide imagery for the early detection of fast-developing severe weather (nowcasting), weather forecasting and climate monitoring.
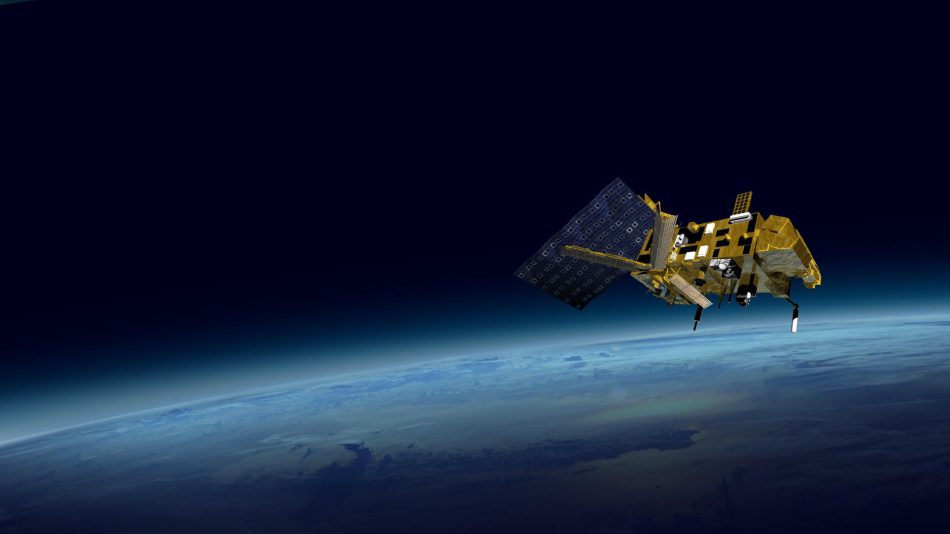


MetOp (LEO) atmosphere monitoring satellites
EUMETSAT is operating the MetOp (Meteorological Operational Program of Europe) satellites that are in operation since 2006. These LEO satellites carry eight main instruments that provide more detailed global data to monitor the atmosphere, oceans and land surfaces as well as the cryosphere.
The MetOp satellites are closer to the Earth in polar orbit (81km above the Earth) providing detailed global observations of the atmosphere, oceans and land. These data are essential for weather forecasting up to 10 days ahead and climate monitoring.
EUMETSAT processes these satellite observations to develop climate data records, which are time series of satellite measurements of sufficient length and consistency to determine climate variability and change. The climate monitoring activities are centralized in Darmstadt in Germany and made available to its Member States, the Copernicus Climate Change Service, and users worldwide, including the global scientific community.
In addition, ocean monitoring satellites such as the Jason-series ((Joint Altimetry Satellite Oceanography Network) and Copernicus Sentinel-6 monitor global mean sea level rise due to climate change, while the Sentinel-3 satellites collect other essential ocean observations in cooperation with ESA.


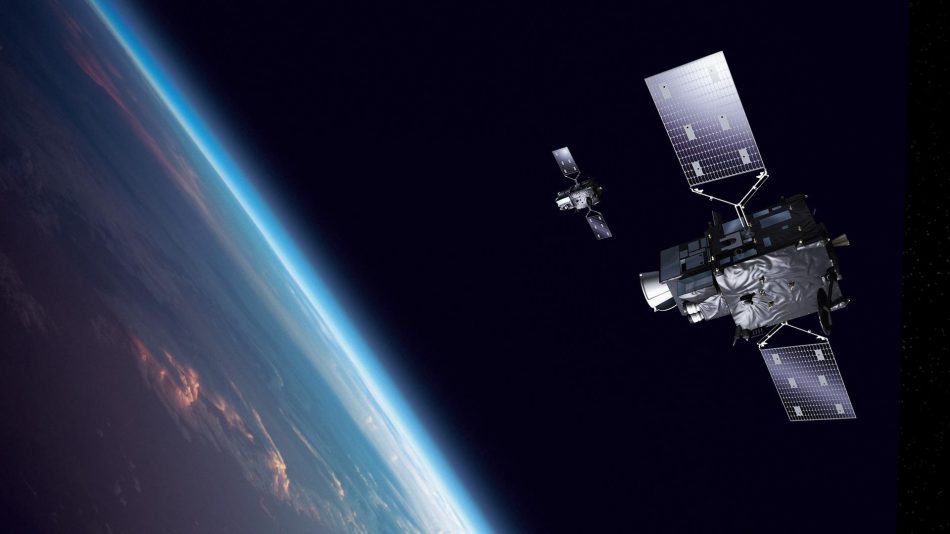
Sentinel Earth monitoring satellites and instruments
EUMETSAT operates, in corporation with ESA, the Copernicus Sentinel-3 and Sentinel-6 satellites as well as operating and delivering products from the Sentinel-4 and Sentinel-5 instruments onboard Meteosat Gen3 and MetOp Gen2 satellites, respectively.
The Copernicus Sentinel-6 provides global sea surface height observations for climate monitoring and ocean and seasonal forecasts continuing a time series of mean sea level rise dating back to 1992. The altimetry instruments also provide measurements of wind speed at the ocean surface and significant wave height.
Other instruments on board the satellite collect high resolution vertical profiles of temperature, using the GNSS Radio Occultation sounding technique, to assess temperature changes in the troposphere and stratosphere and to support Numerical Weather Prediction.
The mission is co-funded by the European Commission, ESA, EUMETSAT and the USA, through NASA and NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration).
EUMETSAT also operates the Sentinel-4 instrument, on board MTG satellite and will monitor air quality over Europe every hour at high spatial resolution. The Sentinel-5 instrument on board MetOp-SG is monitoring global air quality and climate-related trace gases and aerosols in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Jason LEO Earth and climate monitoring satellites
The Jason-series of satellites are providing global sea surface height observations for climate monitoring and ocean and seasonal forecasts. The company currently operates the Jason-3 satellite that helps improve global atmosphere and ocean forecasting. The satellite was launched on January 17th, 2016 by SpaceX and is operational since October 2016.
Jason-3 was constructed by Thales Alenia Space and built on the same cooperation as Jason-2, involving EUMETSAT, NOAA, CNES and NASA, with Copernicus expected to support the European contribution to operations.
Active Satellites
| Satellite | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| Jason-3 | Jason 3 | Jan 17th, 2017 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| MetOp-B | ST25 | Sep 17th, 2012 | Soyuz-2 | Arianespace KAZ |
| MetOp-C | VS19 | Nov 7th, 2018 | Soyuz ST-B | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-9 (MSG-2) | V169 | Dec 22nd, 2005 | Ariane V | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-10 (MSG-3) | VA207 | July 05th, 2012 | Ariane V | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-11 (MSG-4) | VA224 | July 15th, 2015 | Ariane V | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-12 (MSG-I1) | VA259 | Dec 13rd, 2022 | Ariane V | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 1A | VS07 | Apr 3rd, 2014 | Soyuz ST-B | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 2A | VV05 | Jun 22nd, 2015 | Vega | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 3A | Sentinel 3A | Feb 16th, 2016 | Rockot KM | Eurockot GER/RUS |
| Sentinel 1B | VS14 | Apr 25th, 2016 | Soyuz ST-B | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 2B | VV09 | Mar 6th, 2017 | Vega | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 5P | Sentinel 5P | Oct 13th, 2017 | Rockot KM | Eurockot GER/RUS |
| Sentinel 3B | Sentinel 3B | Apr 25th, 2018 | Rockot KM | Eurockot GER/RUS |
| Sentinel 6A | MF (Jason-CS-A) | Nov 21st, 2020 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| Sentinel 2C | Sentinel 2C | July 9th, 2024 | Ariane 6 | Arianespace FG |
| Sentinel 1C | Sentinel 1C | Dec 4th, 2024 | Vega C | Arianespace FG |
Future Satellites
| Satellite | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| MetOp-SG A1 | 2024 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MetOp-SG B1 | 2025 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MetOp-SG A2 | 2031 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MetOp-SG B1 | 2032 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MetOp-SG A3 | 2038 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MetOp-SG B1 | 2039 | Ariane-62 | Arianespace FG | |
| MTG-S1 (Meteosat-13, Sentinel-4A) | 2024 | Ariane-64 | Arianespace FG | |
| MTG-I2 (Meteosat-14) | 2025 | Ariane-64 | Arianespace FG | |
| MTG-I3 (Meteasat-15) | 2032 | Ariane-64 | Arianespace FG | |
| MTG-S2 (Meteosat-16, Sentinel-4B) | 2024 | Ariane-64 | Arianespace FG | |
| MTG-I4 (Meteosat-17) | 2035 | Ariane-64 | Arianespace FG | |
| Sentinel 3C | 2024 | Vega 2 | Arianespace FG | |
| Sentinel 3D | 2025 | Vega 2 | Arianespace FG | |
| Sentinel 6B (Jason-CS-B) | 2025 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA | |
| Sentinel 7A (CO2M-1) | 2025 | Vega 2 | Arianespace FG | |
| Sentinel 7B (CO2M-2) | 2026 | Vega 2 | Arianespace FG | |
| Sentinel 8 (LSTM) | 2029 | |||
| Sentinel 9 (CRISTAL) | 2027 | |||
| Sentinel 10 (CHIME) | 2029 | |||
| Sentinel 11A (CIMR-1) | 2028 | |||
| Sentinel 11B (CIMR-2) | 2028 | |||
| Sentinel 12 (ROSE-L) | ? |
Retired Satellites
| Satellite | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| Jason-1 | Jason/TIMED | Dec 7th, 2001 | Delta II 7920 | Boeing/ULA USA |
| Jason-2 | OSTM/Jason-2 | Jun 20th, 2008 | Delta II 7320 | Boeing/ULA USA |
| MetOp-A | VS04 | Oct 6th, 2006 | Soyuz-ST | Arianespace KAZ |
| Meteosat-1 | Nov 23rd, 1977 | Delta 2914 | Boeing/ULA USA | |
| Meteosat-2 | Meteosat/CAT/Apple | June 10th, 1981 | Ariane I | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-3 | PAS 1/Meteosat | June 15th, 1988 | Ariane 44LP | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-4 (MOP-1) | JCSat-1/MOP-1 | Apr 19th, 1989 | Ariane 44LP | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-5 (MOP-2) | Astra-1/MOP-2 | Mar 2nd, 1991 | Ariane 44LP | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-6 (MOP-3) | Meteosat 6 | Nov 20th, 1993 | Ariane 44LP | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-7 (MTP) | Meteosat 7 | Sep 3rd, 1997 | Ariane 44LP | Arianespace FG |
| Meteosat-8 (MSG-1) | V155 | Aug 28th, 2002 | Ariane V | Arianespace FG |
MOP = Meteosat Operational Program
MSG = Meteosat Second Generation
MTG = Meteosat Third Generation
MetOp = Meteorological Operational Program of Europe
| Member State | Member since | Organization | Website |
| Austria | 1993 | Zentralanstalt für Meteologie und Geodynamik | ZAMG |
| Belgium | 1986 | Koninklijk Meteorologische Instituut van België | KMI |
| Bulgaria | 2014 | National Institute for Meteorology and Hydrology | NIMH |
| Croatia | 2006 | Drzavni hidrometeorloski zavod | DHMZ |
| Czech Rep. | 2010 | Český hydrometeorologický ústav | CHMI |
| Denmark | 1986 | Danmarks Meteorologiske Institut | DMI |
| Estonia | 2013 | Riigi Ilmateenistus | EMHI |
| Finland | 1986 | Ilmatieteen Laitos | FMI |
| France | 1986 | Météo-France | METEO FRANCE |
| Germany | 1986 | Deutscher Wetterdienst | DWD |
| Greece | 1988 | Hellenic National Meteorological Service | HNMS |
| Hungary | 2008 | Országos Meteorológial Szolgálat | OMSZ |
| Iceland | 2014 | Veõurstofa Íslands | IMO |
| Ireland | 1986 | Met Éireann | Met Éireann |
| Italy | 1986 | Ufficio Generale Spazio Aereo e Meteorologia | MeteoAM |
| Latvia | 2009 | Latvijas Vides, Geologijas un Meteorologijas Centrs | LEGMC |
| Lithuania | 2013 | Lietuvos Hidrometeorologijos Tarnyba | LHMT |
| Luxembourg | 2002 | Administration de la navigation aérienne | ANA |
| Netherlands | 1986 | Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut | KNMI |
| Norway | 1986 | Meterologisk Institutt | MET |
| Poland | 2009 | Instytut Meteorologii I Gospodarki Wodnej | IMGW |
| Portugal | 1989 | Instituto Portugues do Mar e da Atmosfera | IPMA |
| Romania | 2010 | National Meteorological Administration of Romania | NMA |
| Slovak Rep. | 2006 | Slovensky hydrometeorologicky ústav | SHMU |
| Slovenia | 2008 | Agencija Republike Slovenije za Ôkolje | SEA |
| Spain | 1986 | Agencia Estatal de Meteorologia | AEMET |
| Sweden | 1986 | Sveriges meteorologiska och hydrologiska institut | SMHI |
| Switzerland | 1986 | MeteoSchweiz | METEOSWISS |
| Türkiye | 1986 | Meteoroloji Genel Müdürlügü | TSMS |
| UK | 1986 | Met Office | METOFFICE |
All trademarks, logos and images mentioned and showed on this page are property of their respective owners.
Resources
www.eumetsat.int
www.esa.int
www.noaa.gov
www.spacex.com
www.nasa.gov
www.cnes.fr
www.wikipedia.org
www.sealevel.jpl.nasa.gov
www.ecmwf.int
www.space.skyrocket.de
www.marine.copernicus.eu
www.airbus.com
www.arianespace.com
www.aerospace-technology.com
www.starsem.com
www.thalesgroup.com
www.spaceflight101.com
www.nanosats.eu
www.nasaspaceflight.com

Supplier
EUMETSAT
EUMETSAT
Eumetsat Allee 1
D-64295 Darmstadt
Germany
Satellite fleet by EUMETSAT
| Satellite | Country | |||
| MSG-1 (Meteosat-8)SmallGEO | 0.0° West | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MSG-2 (Meteosat-9)SmallGEO | 0.0° West | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MSG-3 (Meteosat-10)SmallGEO | 0.0° East | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MSG-4 (Meteosat-11)SmallGEO | 0.0° East | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MTG-I1 (Meteosat-12)SmallGEO | 0.0° West | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MTG-S1 (Meteosat-13, Sentinel-4A)SmallGEO | 0.0° West | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
Smallsats launched by EUMETSAT
| Smallsat | Country | |||
| Sentinel-6B (S6B)LEO | Sentinel-6B | EUMETSAT |  | Climate & Environmental |
| MetOp-SGA1LEO | VA264 / MetOp-SGA1 – Sentinel-5A | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| Jason-3LEO | Jason-3 | EUMETSAT |  | Earth Observation |
| MetOp-ALEO | ST16 / MetOp-A | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MetOp-BLEO | ST25 / MetOp-B | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |
| MetOp-CLEO | VS19 / MetOp-C | EUMETSAT |  | Weather Forecasting |