Back to selection
Satellite
GeoOptics CICERO LEO satellite constellation
Position
LEO
Regions
Asia Pacific Region
Europe Region
Middle East Region
North & Central Africa Region
North America Region
Oceania Region
Russia & CIS Region
South Africa Region
South America Region
Manufacturer
Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems Inc.
Operator
Launch operators
Arianespace GK Launch Services Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) SpaceX
Launch vehicles
Launch date
January 1st, 1970
Expected lifetime
10 Years
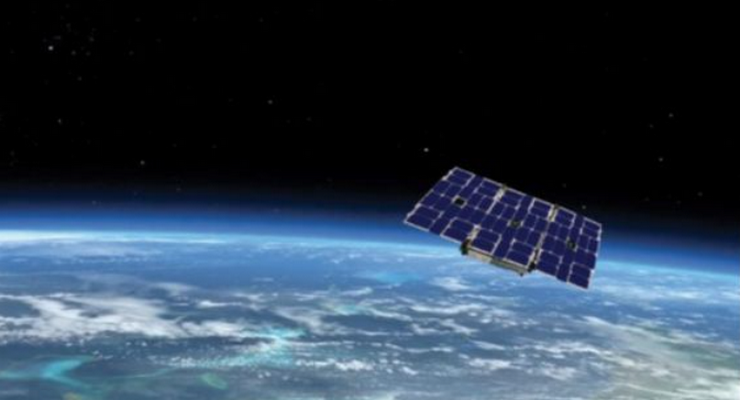

GeoOptics CICERO LEO satellite constellation
The GeoOptics CICERO LEO satellite constellation is operated by GeoOptics, an environmental data company that carries out daily weather forecasting, environmental monitoring, and research activities. The company focuses exclusively on weather data with a constellation of 24 LEO satellites (CubeSats) called CICERO (Community Initiative for Cellular Earth Remote Observation).
Founded in 2006, GeoOptics is privately held and gathers data that solves problems making use of Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signals, such as those from the GPS constellation, to examine the Earth’s atmosphere in fine detail.
The company developed CICERO 115 kg Micro-satellites together with the University of Colorado Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP) using the TriG GNSS-RO payload developed to fly on the FORMOSAT-7/COSMIC-2 mission, a Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere & Climate, an international collaboration between NSPO from Taiwan and the NOAA from the USA. Later during development, the massive miniaturization of the GNSS-RO payload, Cion, allowed the satellite design to be changed to a much smaller 6U CubeSat-based version built by satellite manufacturer Tyvak Nano-Satellite Systems.
The CICERO constellation provides the highest quality radio occultation data that is made available to potential commercial or government customers. The constellation is designed to create the most detailed picture ever assembled of the Earth’s ionosphere, atmosphere, surface and subsurface.
CICERO satellites are launched mainly as secondary payloads and with RideShare launches:
- CICERO 6 was the company’s first satellite and was launched in June 2017 on a PSLV-XL rocket operated by ISRO from India. Three more satellites, the CICERO 1, -2 and -3 followed in July of that same year on a Russian Soyuz-2-1a Fregat booster, operated by GK Launch Services. Reportedly these three satellites are all inoperative after deployment.
- On January 12th, 2018 the CICERO 7was successfully launched from India on a PSLV-XL rocket, operated by ISRO.
- One more satellite,the CICERO 10 (Tyvak-0086), was launched in November 2018 from New Zealand on an Electron KS rocket operated by SmallSat launch operator Rocket Lab.
- CICERO 8 (Tyvak-0076) was launched in November 2018 on ISRO’s PSLV-CA launcher from India.
- On September 3rd, 2020 the OSM-1/CICERO(Tyvak-0088) CubeSat was launched on a Vega rocket operated by Arianespace from the Kourou launch base in French Guiana.
- On May 25th, 2022 launch operator SpaceX orbited CICERO-2/VEH 1 and CICERO-2/VEH 2 CubeSats with their Transporter-5 RideShare mission with a Falcon 9 rocket. The spacecraft are the first phase of GeoOptics’s CICERO-2 constellation, which form a unified Earth observatory allowing governments, industry, and individual stakeholders to monitor and prepare for the many impacts of climate change.
Satellite Mission Launch Date Launcher Launch Operator CICERO 1 Canopus-V-IK July 14th, 2017 Soyuz-2 GK Launch RUS CICERO 2 Canopus-V-IK July 14th, 2017 Soyuz-2 GK Launch RUS CICERO 3 Canopus-V-IK July 14th, 2017 Soyuz-2 GK Launch RUS CICERO 4 na CICERO 5 na CICERO 6 PSLV-C38/CartoSat-2 June 23rd, 2017 PSLV-XL ISRO India CICERO 7 (Tyvak-0085) PSLV-C40/CartoSat-2 Jan 12th, 2018 PSLV-XL ISRO India CICERO 8 (Tyvak-0076) PSLV-C43/HysIS Nov 29th, 2018 PSLV-CA ISRO India CICERO 9 na CICERO 10 (Tyvak-0086) ‘It-Is-Business-Time’ Nov 11th, 2018 Electron Rocket Lab NZ CICERO 11 na CICERO 12 na OSM-1 (Tyvak-0088) VV-16 Sept 3rd, 2020 Vega Arianespace FG CICERO-2/VEH 1 Transporter-5 May 25th. 2022 Falcon 9 SpaceX USA CICERO-2/VEH 2 Transporter-5 May 25th. 2022 Falcon 9 SpaceX USA
Satellite
GeoOptics CICERO LEO satellite constellation
Satellite
GeoOptics CICERO LEO satellite constellation
Satellite