O3b Networks
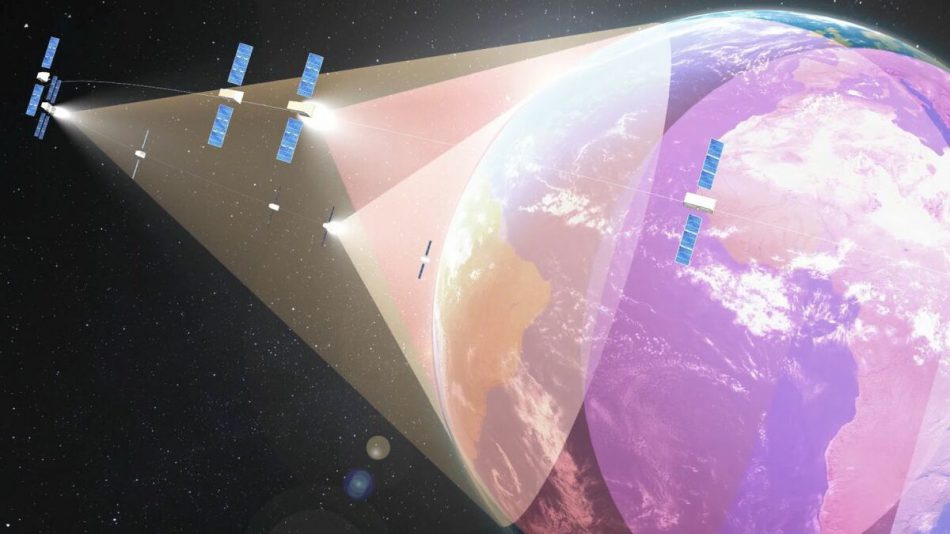
O3b Networks (SES Networks) was a global satellite service provider operating a constellation of 12 Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites, servicing telecommunications operators, Internet service providers and enterprise and government customers in Latin America, Africa, the Middle-East and the Asia Pacific. O3b is short for the “other 3 billion” people that do not have ready access to the Internet. Due to its close proximity to earth at 8,000 km above the earth versus geostationary orbit at approximately 36,000km, O3b’s system combines the global reach of satellite with the speed of a fibre-optic network to provide low-cost, low-latency (the amount of time taken for information to be sent from one location to another), high-throughput internet and mobile connectivity to its customers.
Watch the video: O3b is the fastest growing satellite operator in history!
O3b was head quartered in St. Helier, Jersey with an operational head office in The Hague, Netherlands. In 2016 O3b Networks became a wholly owned subsidiary of satellite operator SES S.A. O3b Networks was renamed as SES Networks, a division of SES. The satellites themselves, now part of the SES fleet, continue to use the O3b name.
Till 2018 O3b operated a constellation of 16 MEO Ka-band High Throughput Satellites (HTS), each capable of 1.6 Gigabits per second (Gbps) with a latency of less than 150 milliseconds. The constellation entered commercial operations in September 2014, and Thales Alenia Space is currently building a follow-on series of eight more spacecraft.
The network combines the relatively large reach of satellite with high speed and medium latency (the amount of time taken for information to be sent from one location to another) to deliver satellite Internet services and mobile backhaul services to emerging markets.
After initially planning to launch in 2010, the first four satellites were launched on June 25th, 2013 on a Soyuz launch vehicle of launch operator Arianespace. A further four satellites were launched in July 2014, and another four in December 2014, all by an Arianespace Soyuz rocket. Four more were launched in March 2018 and another four were successfully launched in April 2019, bringing the constellation to 20 satellites, including the three current satellites which will be used as in-orbit backup.
In September 2017, SES announced the next generation of O3b satellites (mPower-series) and placed an order for an initial seven from satellite manufacturer Boeing Defense & Space, expected to launch in 2021, the O3b mPower constellation of MEO satellites for broadband Internet services will “be able to deliver anywhere from hundreds of megabits to 10 gigabits to any ship at sea” through 30,000 spot beams. Software-defined routing will direct traffic between the mPower MEO satellites and SES’ geostationary fleet.

History of O3b
The company was founded in 2007 by former Google executive and satellite-industry veteran, Gregory Thane Wyler. O3b was financially backed by SES, Google, HSBC, Liberty Global, Allen & Company, Northbridge Venture Partners, Soroof International, Development Bank of Southern Africa (DBSA), Sofina and Satya Capital.
In the mid-2000’s, Greg Wyler was in Africa trying to determine how to bring people better Internet access. In 2003 he was was working with RwandaTel building up a local team and connected over 200 schools to the Internet, providing Fiber-to-the -Home (FTTH) with a 3G network centered principally in Rwanda. Wyler took then 99% control of Rwandatel through his communication firm Terracom that was sold to the Rwanda Government in 2006 for 20 million USD.
The challenge of overcoming infrastructure limitations led to the idea of O3b Networks. Wyler landed on bringing satellites closer to the Earth as the solution for this problem, and designed a system that would quickly bring high throughput capacity to telecom headends using Ka-band spectrum. He embarked on creating the Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) system aimed at connecting the “Other 3 Billion”, the number of people living without Internet access at the time of founding. The Great Recession threatened to derail the startup, but the O3b team managed to get the funding necessary to progress.
In November 2010, the company raised a total of 1.2 billion USD from a group of investors and banks to fully finance the construction of its satellites. The funding was sourced from a diverse mix of investors, including strategic shareholders, commercial banks and developmental finance institutions, including the DBSA.
In 2011 Mark Rigolle, former Chief Finance Officer of SES and O3b CEO since 2010, returned to SES. In his place, Steve Collar joined from SES World Skies where he had served as Senior Vice President of Business and Market Development and was formerly an O3b board member representing SES’ interests. This change marks the fifth CEO for O3b in three years.
In July 2017 Rigolle was requested to lead start-up US-based LeoSat when this company established its first European office in The Hague in The Netherlands.
In July 2014, SES subsidiary SES Government Solutions (SES GS) received approval to offer O3b services to the US Government. Later on, in August 2016, SES GS supported the US Department of Defense with O3b Networks high throughput, low latency satellite communications solutions.
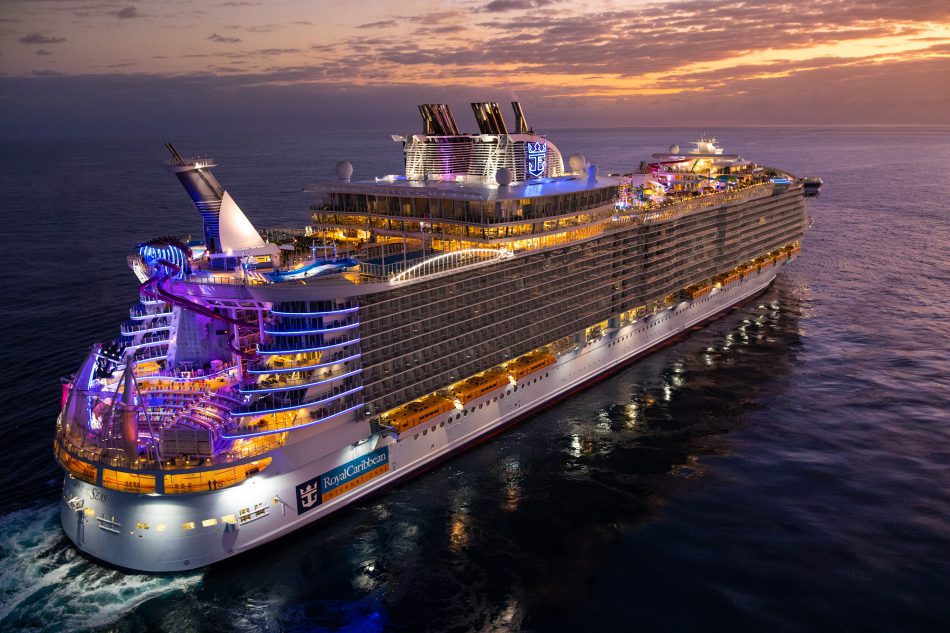
In November 2014, MS Oasis of the Seas which is the world’s largest cruise ship carrying 8,000 passengers and crew, became the first cruise ship to provide fast Internet to guests through O3b Networks. The service has been rolled out to every ship of the Royal Caribbean International fleet.


In March In August 2015, SES GS agreed a one-year contract with US government scientific agency, NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) to supply O3b services and ground equipment to the National Weather Service Office in American Samoa, which will expand NOAA’s broadband connectivity outside the continental US to provide weather, water, and climate data and forecasts and warnings to American Samoa.
In August 2015 O3b Networks ordered more satellites and new antennas to bolster its Ka-band High Throughput Satellite (HTS) network in the near future. The company also intends to increase its capacity in space in the near future. In addition to new satellites, new antenna systems are also under development; a land transportable antenna system developed by mobile antenna manufacturer AVL Technologies, Inc.
In March 2016 satellite operator SES made a 20 million USD investment in O3b, increasing SES’ ownership from 49.1% to 50.5% resulting in further collaborative satellite services between SES’ GEO satellites and the O3b constellation. In May 2016 SES invested another 710 million USD to acquire all shares taking full ownership of O3b Networks.
Also in March 2016 O3b was recognized as Satellite Operator of the Year in the 2015.
SES placed an order in 2017 with satellite manufacturer Boeing Defense & Space for seven 2nd-generation satellites for a constellation called O3b mPower, designed to deliver 10 terabits of throughput. O3b mPower-series of satellites are scheduled for launch in 2021.
In 2018 four satellites were launched by Arianespace on a Soyuz launch vehicle and are part of an eight-satellite order O3b Networks placed with satellite manufacturer Thales Alenia Space, prior to SES ownership. The other four satellites were successfully launched in April 2019 on another Arianespace Soyuz launch vehicle.
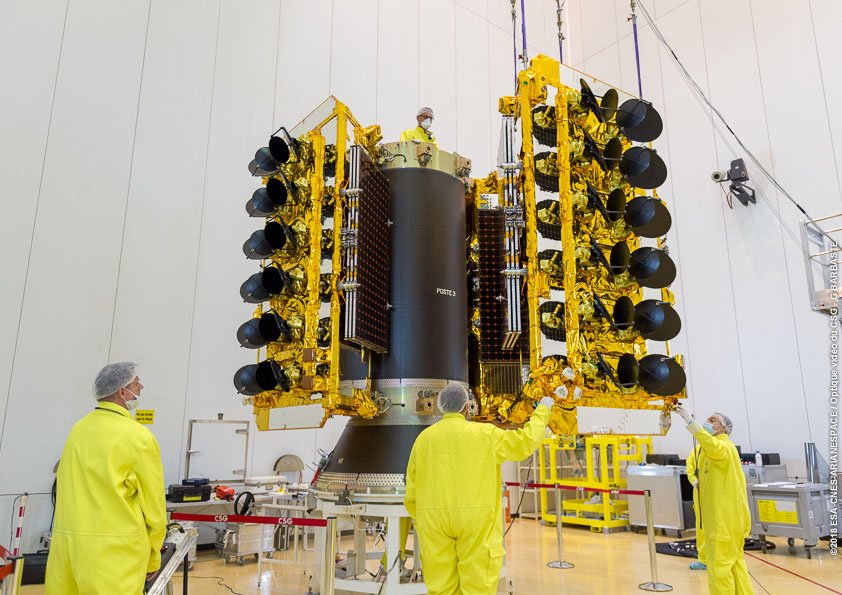
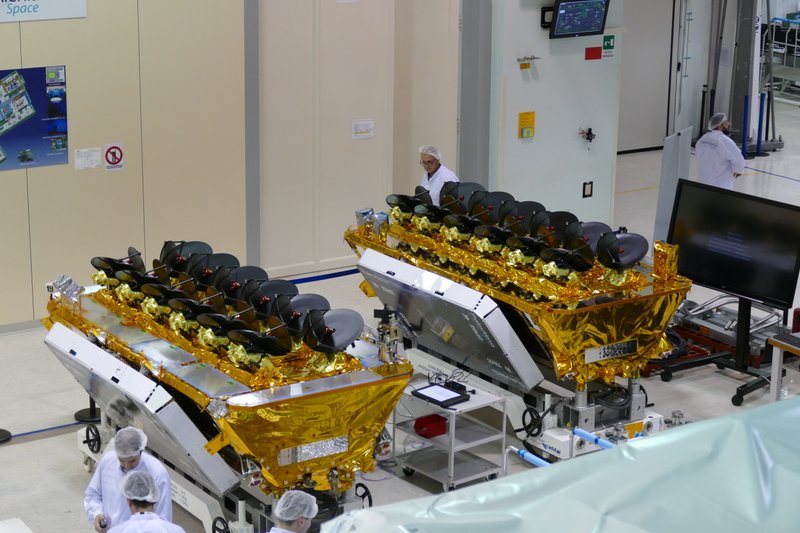
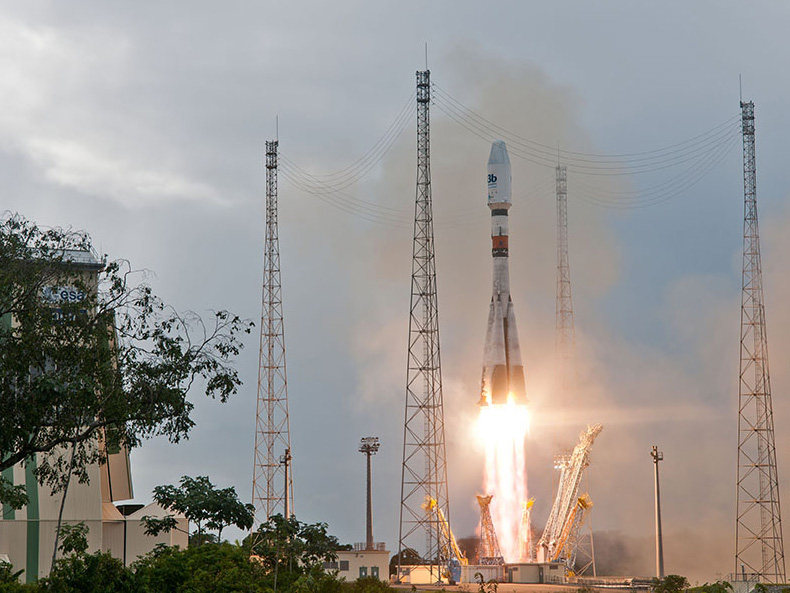



O3b Satellite launches
In September 2008 satellite launch operator Sea Launch signed a launch services agreement with O3b Networks for up to two launches of O3b’s Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellite constellation scheduled in 2010. The O3b satellites were deployed by Sea Launch’s Zenit-3SL system in groups of eight per launch. Sea Launch is developing a new multi-spacecraft dispenser for these missions, which will accommodate O3b Networks’ specific orbital insertion requirements.
In 2009 Sea Launch filled for bankruptcy and was not able to meet its contractual obligations. In March 2010 O3b Networks cancelled the launch contract with Sea Launch and switched to Arianespace to launch the satellites on Soyuz rockets from the Kourou launch site in French Guiana at the time, the first launch was apparently planned in 2012.
O3b’s first four satellites (FM1, FM2, FM4 & FM5) were launched on a Soyuz-2/Fregat-MT rocket by launch provider Arianespace on June 25th, 2013 and are currently in orbit and functioning properly. After discovering a hardware defect in the initial satellites, O3b postponed the planned September 2013 launch of four additional satellites so repairs could be made.
The second set of four satellites (FM3, FM6, FM7 & FM8) were also launched by Arianespace on a Soyuz launch vehicle from the Space Center in French Guiana, on July 10th, 2014.
The third launch of four satellites (FM9, FM10, FM11 & FM12) took place in December 2014 on Arianespace’ Soyuz launch vehicle. Watch the video of the Arianespace launch on their Soyuz launch vehicle:
On March 9th, 2018 four additional satellites (FM13, FM14, FM15 & FM16) were launched by Arianespace on a Soyuz launch vehicle to join the existing constellation of 12.
On April 4th 2019 four additional satellites (FM17, FM18, FM19 & FM20) were launched by Arianespace on a Soyuz launch vehicle to join the existing constellation of 16.
All trademarks, logos and images mentioned and showed on this page are property of their respective owners.
Resources
www.ses.com
www.satellitetoday.com edition September 23rd, 2008
www.satellitetoday.com edition August 18th, 2015
www.capacitymedia.com edition August 26th, 2015
www.satellitetoday.com edition March 5th, 2016
www.businesswire.com edition April 29th, 2016
www.spacenews.com edition March 9th, 2018
www.interactive.satellitetoday.com
www.dbsa.org
www.rwandatel.rw
www.marinesatellitesystems.com
www.sealaunch.com
www.arianespace.com
www.dailywireless.org
www.thehagueonline.com
www.spaceflight101.com
www.sky-brokers.com
www.nasaspaceflight.com
www.satyacapital.com
www.bloomberg.com
www.wikipedia.org
www.youtube.com
www.space.skyrocket.de
www.bluesky.co.uk
www.russianspaceweb.com
