
Back to selection

Supplier
Spire Global
Spire Global, Inc.
251 Rhode Island Street, Suite 204
San Francisco, CA 94103
USA
Spire Global is a space-to-cloud CubeSat satellite operator that is specialized in the tracking of unique data sets from the Earth powered by a large constellation of small LEO satellites (nano-satellites), the Low Earth Multi-Use Receiver (LEMUR) CubeSat platform. Spire analyzes data from the tracking of maritime, aviation and weather patterns.
The company operates a fleet of more than 110 CubeSats, the second largest commercial constellation by number of satellites and the largest by number of sensors. The satellites are integrally designed and built by Spire. It has launched more than 140 satellites to orbit since the creation of the company in 2012.
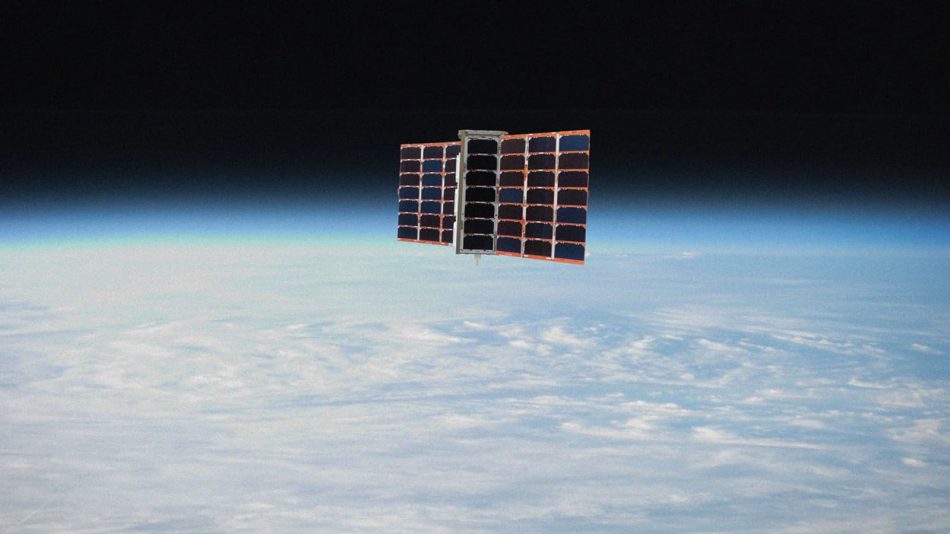

Spire Global is headquartered in San Francisco, USA and has offices in Boulder, Washington in the USA, Glasgow in the UK, Luxembourg and Singapore.
Company History
Spire Global was originally known as NanoSatisfi, Inc. that was established in 2012 in San Francisco, USA. Three International Space University Graduates, Peter Platzer, Jeroen Cappaert and Joel Spark started the ArduSat projectto ‘democratize access to space’. ArduSat was partly financed thru the public crowdfunding platfom KickStarter and raised 100,000 USD.
In 2013 Spire partnered with Lemnos Labs in order to raise additional capital required for the manufacturing of the ArduSat-1 and ArduSat-2 (1U CubeSat) satellites. In February 2013 funds of 1.5million USD were raised by Investment and space companies such as Shasta Ventures, Lemnos Labs, E-merge, Grishin Robotics, and Beamonte Investments.
In November 2013 both ArduSat-1 and ArduSat-X were successfully released from the Japanese Kibō Experiment Module of the ISS and quickly started transmitting data to Spire servers.
Following this experimentation, Spire engineers opted to focus on 3U nanosatellites to start porting more complex payloads In June 2014 the first iteration of its standard satellite format, LEMUR-1, was launched with the Dnepr rocket, a modified Ukrainian missile known as the R-36M operated by ICS Kosmotras.
In July 2014 Spire Global announced another 25 million USD of funding that was led by Venture Capitalists. In August 2014 the company announced that ArduSat would be spun-off of the company and would focus exclusively on educational technology in partnership with U.S. high schools. Also, in 2014, Spire opened its Singapore office and started steadily increasing its network of ground stations.
LEMUR Satellite Constellation
LEMUR-2 is the initial constellation of low-Earth orbiting satellites built by Spire. These satellites carry two payloads for meteorology (SENSE payload) and ship AIS traffic tracking (STRATOS payload). Later satellites, beginning with the 78th satellite launched, carry also the AirSafe ASD-B payload to track airplanes.
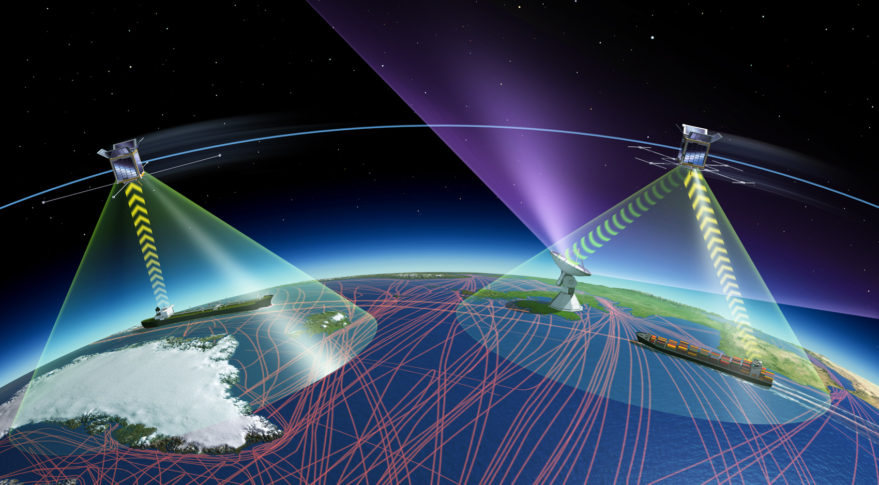


The LEMUR-2 satellites are launched in small batches as secondary payloads on various rocket boosters executed by reputed launch providers:
- On September 28th 2015 the first four more LEMUR-2 satellites were launched as a piggy-back on the AstroSat mission on a PSLV launcher, operated by ISRO from India.
- Spire’s second batch of LEMUR-2 satellites was launched on March 22nd 2016 with the Cygnus CRS-6 cargo ship atop an Atlas V booster operated by ULA to be launched to the ISS. The mission was flown for Orbital ATK (Lockheed Martin) under NASA’s Commercial Resupply Services contract. With a payload of more than 16,000 pounds it was the heaviest payload to date launched on an Atlas V.
- Four of the satellites were deployed from the ISS airlock, five of them directly from the NanoRacks NRCSD-E deployer on the Cygnus vehicle. Deployment of the ISS satellites began on May 18th 2016. Four of the five other satellites were deployed on June 22nd from Cygnus, but the fifth failed to deploy and re-entered together with Cygnus.
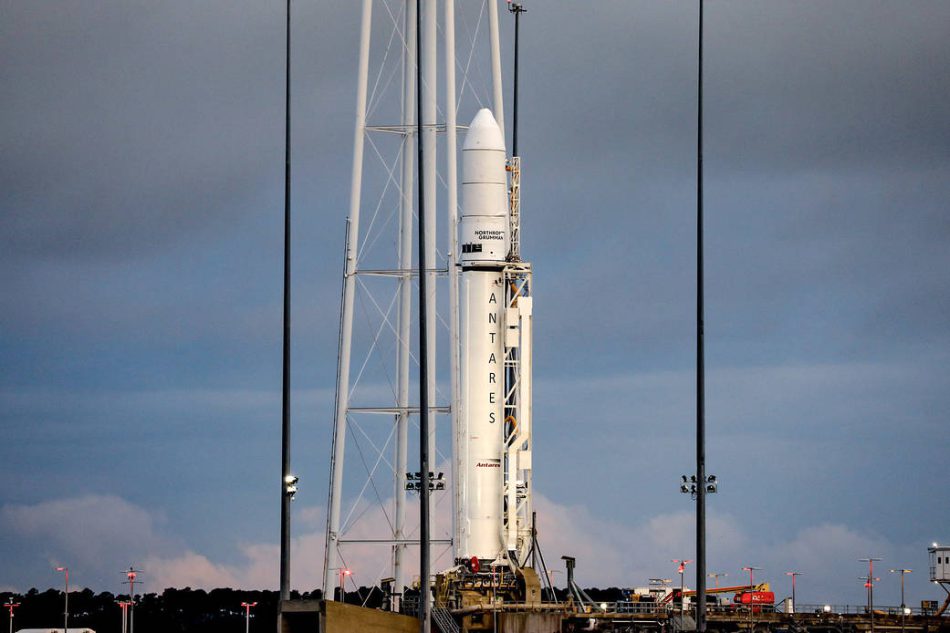
- The third batch of four satellites was launched on September 17th 2016 on an Antares 230 rocket booster operated by Orbital ATK (Lockheed Martin) in a NanoRacks CubeSat Deployer (NRCSD, NRCSD-E deployer on the Cygnus CRS-5 cargo craft to be deployed after the departure from the ISS.
- A fourth batch of four LEMUR CubeSats was launched in February 2017 on a H-IIB launch vehicle operated by MHI Launch Services from Japan. The batch was transported with a HTV (H-2 Transfer Vehicle) or Kounotori and was launched to the ISS to be deployed from there.In February 2017 eight more satellites followed on a bulk CubeSat launch on an Indian PSLV operated by ISRO.
- In April 2017, four more LEMUR CubeSats followed on the Cygnus CRS-7 mission, launched on an Antares launcher operated by Orbital ATK (Lockheed Martin).


- Another batch of eight LEMUR CubeSats was launched on June 23rd 2017 on an PSLV rocket operated by ISRO from India.
- Another eight were launched on July 14th, 2017 on a Russian Soyuz-2-1a Fregat rocket with 73 CubeSats, operated by GK Launch Services, from the Baikonur launch site in Kazachstan. One of the CubeSats was deployed in a wrong and usable orbit.
- Spire Global scheduled a launch of another eight LEMUR-2 CubeSats into orbit on the ORS 5 (Operationally Responsive Space 5) or SensorSat mission on an Orbital ATK Minotaur-4/Orion-38 (a.k.a. OSP-2 Peacekeeper SLV) rocket, but had to cancel the launch due to legal issues concerning the restriction on the use of excess ballistic missile assets for commercial payloads.
- On November 12th, 2017 Spire launched another eight satellites onboard of the Cygnus CRS-8 transport vehicle on Orbital ATK’s Antares-230 rocket, to be deployed after the Cygnus departs the ISS.
- On November 28th 20-17 another batch of ten CubeSat satellites was launched as co-passengers on a Soyuz-2-1b Fregat rocket, operated by GK Launch Services but were lost due to an upper stage problem.
On January 12th 2018 a batch of six satellites was launched on a PSLV rocket operated by ISRO from India.
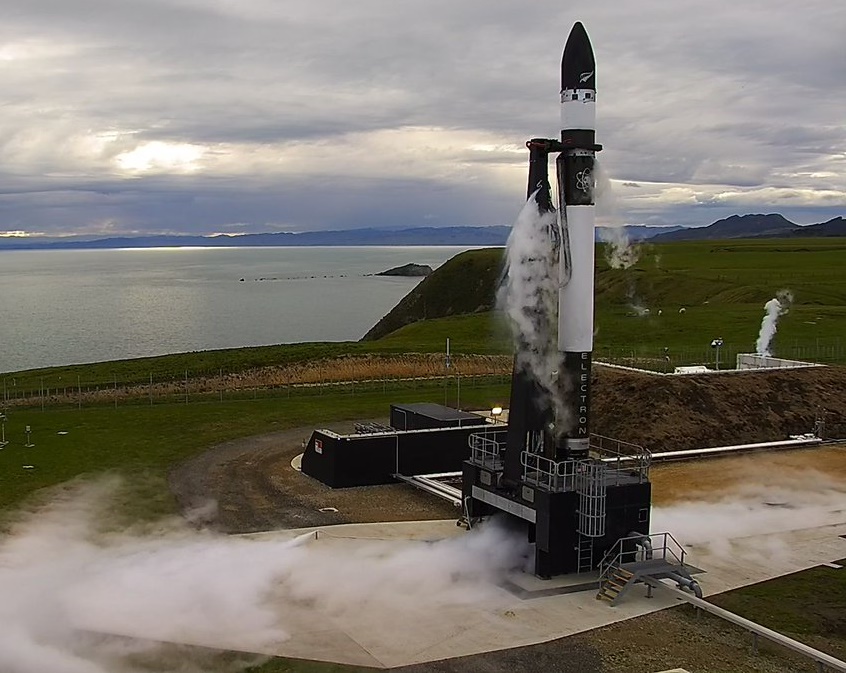
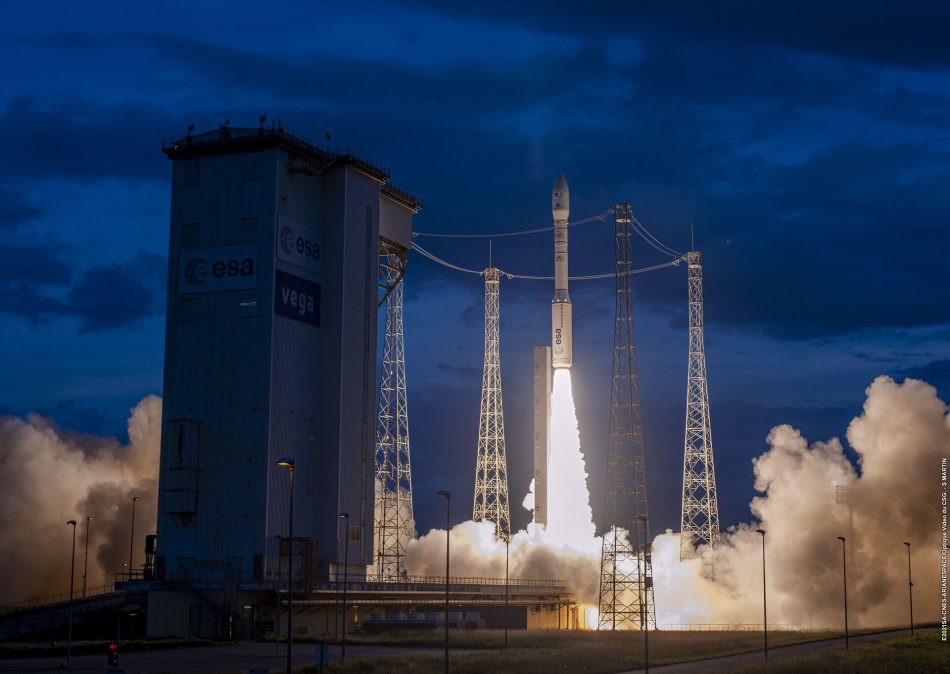



- Two LEMUR CubeSats were launched on January 21st 2018 on the second launch of the Electron KS launcher operated by Rocket Lab.
- Four more satellites were orbited on February 1st 2018 on a Soyuz-2-1a Fregat, executed by GK Launch Services, from the Baikonur launch site in Kazachstan.
- On May 21st 2018 four satellites were launched onboard of the Orbital ATK’s Cygnus CRS-9 space craft on an Antares-230 rocket to be deployed after the Cygnus departs the ISS. These were the first LEMUR-2 satellites enabled to receive Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) signals for Aircraft.
- Two satellites were launched on November 11th, 2018 on an Electron launcher, operated by launch provider Rocket Lab from the launch base on the Mahai Peninsula in New Zealand.
- Four more LEMUR CubeSats followed on November 29th 2018 on a PSLV rocket operated by ISRO from India. Two of them were sponsored by ESA under the ARTES Pioneer program.
- On December 27th 2018, eight LEMUR CubeSats were launched on a Soyuz-2-1a Fregat, operated by GK Launch Services from the Vostochny Cosmodrome launch site in Kazachstan.
- On April 1st 2019 four LEMUR’s were launched on a PSLV rocket operated by ISRO from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in India.
- Another eight LEMUR CubeSats were launched on July 5th 2019 on a Soyuz-2-1b Fregat launcher operated by GK Launch Services.
- Four LEMURs CubeSats were launched in December 11th 2019 on a PSLV rocket operated by ISRO.
- On September 2nd 2020 launch operator Arianespace launched eight LEMUR CubeSats on their Vega launcher from the Kourou Spaceport in French Guiana. Two of the satellites failed to deploy and re-entered with the upper stage.
- In September 2020 four LEMUR CubeSats were launched on a Soyuz-2-1b Fregat operated by GK Launch Services.
- Six LEMURs were launched on June 30th 2021 on a Falcon 9 v1.2 rocket operated by launch operator SpaceX. Two CubeSats were deployed directly from the launch vehicle, three from Sherpa-FX 2 and one CubeSat from Sherpa-LTE 1, both free flying satellite deployer developed by Spaceflight, Inc.
- On April 29th 2021 Spire successfully deployed two new satellites into its LEMUR constellation. Launch operator Arianespace launched its Vega rocket and brought Spire to 143 total satellites launched, with more than 110 currently in orbit. This is the second launch of 2021 for Spire and 30th launch overall.
- On May 25th , 2022 another 5 CubeSats were launched with SpaceX’ fifth Rideshare Program mission Transporter-5. The company’s Space-as-a-Service (SPaaS) business, had satellites and hardware onboard the launch for:
- HANCOM inSPACE, initially a spin-off by Korea Aerospace Research Institute and now a part of HANCOM Group, will host an optical payload on a Spire 6U satellite. This will be the first commercial satellite mission for a private South Korean company.
- Myriota, a provider of global Internet of Things (IoT) service from satellites, will use software-defined radios onboard three Spire satellites to quickly and cost-effectively scale its network to offer global, low-latency IoT coverage. Last year, Myriota deployed its software on existing Spire satellites to expand its IoT coverage in a matter of weeks.
- Spire also launched two 3U satellites that will support the demonstration of radio frequency (RF) signals detection and geolocation of L-Band frequencies. The technology demonstration was funded by the Defense and Security Accelerator (DASA), part of the UK Ministry of Defense.
| # satellites | Mission | Launch Date | Launcher | Launch Operator |
| ArduSat-1 | HTV/Kounotori-4 | Nov 19th, 2013 | H-IIB | MHI Launch S. Japan |
| ArduSat-X | HTV/Kounotori-4 | Nov 19th, 2013 | H-IIB | MHI Launch S. Japan |
| 1 | LEMUR-1 | Jun 19th, 2014 | Dnepr | ICS Kosmotras |
| 4 | AstroSat | Sep 28th, 2015 | PSLV-C30 | ISRO India |
| 8 | OA-6 | Mar 22nd, 2016 | Atlas V | ULA USA |
| 1 | Deploy faulure | Mar 23rd, 2016 | Atlas V | ULA USA |
| 4 | Cygnus CRS-5 | Oct 17th, 2016 | Antares 230 | Orbital ATK/LM USA |
| 4 | Kounotori-6 | Sep 12th, 2016 | H-IIB | MHI Japan |
| 8 | CartoSat-2 | Feb 15th, 2017 | PSLV-C37 | ISRO India |
| 4 | OA-7 | Apr 18th, 2017 | Atlas V | ULA USA |
| 8 | CartoSat-2 | JUn 23rd, 2017 | PSLV-C38 | ISRO India |
| 8 | Kanopus-V-1K | Jul 14th, 2017 | Soyuz-2 | GK Launch Russia |
| 8 | Launch failure | Nov 12th, 2017 | Antares 230 | Orbital ATK/LM USA |
| 8 | Meteor-M 2-1 | Nov 28th, 2017 | Soyuz-2 | GK Launch Russia |
| 4 | CartoSat-2 | Jan 12th, 2018 | PSLV-C40 | ISRO India |
| 2 | ‘Still-Testing’ | Jan 21st, 2018 | Electron | Rocket Lab NZ |
| 4 | HysIS | Nov 29th, 2018 | PSLV-C43 | ISRO India |
| 8 | Kanopus-V | Dec 27th, 2018 | Soyuz-2 | GK Launch Russia |
| 4 | MicroSat-R | Jan 24th, 2019 | PSLV-C44 | ISRO India |
| 8 | Meteor-M 2-2 | Jul 5th, 2019 | Soyuz-2 | GK Launch Russia |
| 4 | RiSAT-2BR1 | Dec 11th, 2019 | PSLV-C48 | ISRO India |
| 8 | VV16 | Sep 2nd, 2020 | Vega | Arianespace |
| 4 | Gonets-Mx | Sep 28th, 2020 | Soyuz-2 | GK Launch Russia |
| 2 | May 11th, 2020 | ISS | ||
| 4 | EOS-1 | Jul 11th, 2020 | PSLV-C49 | ISRO India |
| 8 | Transporter-1 | Jan 24th, 2021 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 2 | VV18 | Apr 29th, 2021 | Vega | Arianespace FG |
| 5 | Transporter-2 | Jun 30th, 2021 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 4 | Transporter-3 | Apr 1st, 2022 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 5 | Transporter-5 | May 25th, 2022 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 6 | Transporter-6 | Jan 3rd, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 3 | Transporter-8 | Jun 12th, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 3 | ‘Baby-Come-Back’ | July 18th, 2023 | Electron | Rocket Lab NZ |
| 8 | Transporter-9 | Nov 11th, 2023 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 4 | ‘Four-Of-A-Kind’ | Jan 18th, 2024 | Electron | Rocket Lab NZ |
| 2 | Transporter-10 | Mar 4th, 2024 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| Hubble-1 | Transporter-10 | Mar 4th, 2024 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| Hubble-2 | Transporter-10 | Mar 4th, 2024 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| 4 | Transporter-11 | Aug 16th, 2024 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
| Hubble-3 | Transporter-11 | Aug 16th, 2024 | Falcon 9 | SpaceX USA |
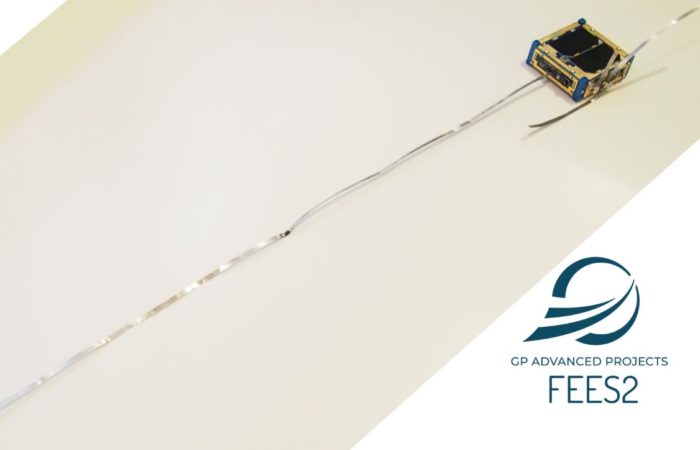
In November 2021 the company signed an agreement with CubeSat satellite launch deployer NanoRacks for the deployment of two 0.3U CubeSat satellites in what was to become “the first U.S. Commercial Satellite Deployment from the International Space Station (ISS). The satellite, named FEES2 (Flexible Experimental Embedded Satellite-2), was developed by the Italian company GP Advanced Projects and is approximately the thickness of a cherry. It will be one of the smallest trackable objects deployed directly from ISS.


In late November 2021, Spire acquired exactEarth, Ltd, a leading provider of global maritime vessel data for ship tracking and maritime situational awareness solutions. After the merger, exactEarth will be fully owned by Spire and will become a subsidiary operating from Cambridge, Ontario, Canada.
On June 28th, 2023 the company announced an extended partnership with satellite operator OroraTech from Germany. The objective of this collaboration is to jointly develop, launch, and operate a constellation of eight satellites exclusively designed for global temperature monitoring. This groundbreaking initiative aims to establish one of the earliest and most extensive constellations dedicated to the tracking and monitoring of wildfires worldwide. Once deployed and fully operational, this constellation will play a pivotal role in enhancing our ability to observe and respond to wildfires on a global scale.
In February 2025 the Canadian Space Agency awarded Spire Global Canada and OroraTech a 50 million USD contract to design and develop a dedicated satellite constellation to monitor wildfires in Canada. This project is part of the WildFireSat mission to enhance wildfire detection and response. Spire will partner with OroraTech to develop the payloads for the constellation, which is scheduled for launch in 2029. It will operate for at least five years under the management of the Canadian Space Agency.
All trademarks, logos and images mentioned and showed on this page are property of their respective owners.
Resources
www.spire.com
www.earth.esa.int
www.nanoracks.com
www.space.skyrocket.de
www.businesswire.com
www.wikipedia.org
www.ulalaunch.com
www.spaceflightnow.com
www.arianespace
www.isro.gov.in
www.spacex.com
www.spacewatch.global edition September 15th, 2021
www.exactearth.com
www.rocketlabusa.com
www.gklaunch.ru
www.satellitetoday.com edition June 29th, 2023
www.satellitetoday.com edition February 7th, 2025

Supplier
Spire Global
Spire Global, Inc.
251 Rhode Island Street, Suite 204
San Francisco, CA 94103
USA
Smallsats launched by Spire Global
| Smallsat | Country | |||
| LEMUR-2 (Mario-Sousa)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Callum-K J)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Gram-E Sue)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Sonnenblume)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Kate)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Fikretdengiz)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (HCS-Bazus)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Wobler)LEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| HyMS IODLEO | Twilight-1 | Spire Global |  | Weather Forecasting |
| LEMUR-2 234 (Hotspur-Tom)LEO | Transporter-15 | Spire Global |  | AIS |
| LEMUR-2 233 (Tartiflette)LEO | Transporter-15 | Spire Global |  | AIS |
| LEMUR-2 232 (Starlight)LEO | Transporter-15 | Spire Global |  | AIS |
| LEMUR-2 227 (Stas-Gorbuk)LEO | Transporter-15 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 226 (DeanandMaeve)LEO | Transporter-15 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Affie-Wauwie)LEO | Bandwagon-4 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Hubble-7 (LEMUR-2 Stitch)LEO | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Hubble-6 (LEMUR-2 Lilo)LEO | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Krish)LEO | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | AIS |
| LEMUR-2 (Sejoung-2 / Hancom-2)LEO | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | AIS |
| Hubble-5 (LEMUR-2 Shaggy)LEO | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Hubble-4 (LEMUR-2 Scooby) | Transporter-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Leia-Philip)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (DELOITTE-1)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Lia-Martin)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (EmersonRose)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (TheFalconer)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Marache-Fran)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Balto)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Sentinel)LEO | Transporter-13 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (GregRobinson)LEO | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| FindusAdler-2 (LEMUR-2 – SpaceGus) | Transporter-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| ArduSat-2 | Cygnus CRS-1 (Orb-1) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| ArduSat-X | HTV-4 (Kounotori-4) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| ArduSat-1 | HTV-4 (Kounotori-4) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 67LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 66LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 65LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 64LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 63LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 62LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 61LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 60LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 59LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 58LEO | Meteor-M 2 №1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Lynsy-Symo)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Lisasaurus)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Sam-Amelia) | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (McPeake) | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (KungFoo)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (LucyBryce)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (XueniTerence)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (ShainaJohl)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Dembitz)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (PeterG)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (AndiS)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Zachary)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Furiaus)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Monson)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (ArtFischer)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Greenberg)LEO | Kanopus-V №IK | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Tachikoma)LEO | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Noguescorreig)LEO | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mia Grace)LEO | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Smita-Sharad)LEO | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Rdeaton)LEO | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Satchmo) | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Spire Minions) | PSLV-C37 / CARTOSAT-2D | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jobanputra) | HTV-6 (Kounotori-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Dunlop) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (McCullagh) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Liu-Poh-Chun) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (RocketJonah) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (RomaCoste) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Brian Davie) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Kevin) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (YongLin) | Cygnus NG-08 (OA-08E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Redfern-Goes) | HTV-6 (Kounotori-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Austintacious) | HTV-6 (Kounotori-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Trutnahd) | HTV-6 (Kounotori-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Trutna) | HTV-6 (Kounotori-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (RobMoore)LEO | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (SpiroVision) | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Angela) | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jenny Barna) | OA-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Daisy-Harper) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (NatalieMurray) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (SarahBettyBoo) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Tinykev) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Zo) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (ChristinaHolt) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Gustavo) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Remy-Colton) | Kanopus-V №5 and №6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (UramChanSol) | Kanopus-V №3 and №4 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jin-Luen) | Kanopus-V №3 and №4 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (TheNickMolo) | Kanopus-V №3 and №4 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Kadi) | Kanopus-V №3 and №4 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Vu) | Cygnus NG-09 (OA-09E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Alexander) | Cygnus NG-09 (OA-09E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Yuasa) | Cygnus NG-09 (OA-09E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (TomHenderson) | Cygnus NG-09 (OA-09E) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (BrownCow) | PSLV-C40 / CARTOSAT-2F | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (McCafferty) | PSLV-C40 / CARTOSAT-2F | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Dave Wilson) | PSLV-C40 / CARTOSAT-2F | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (PW) | PSLV-C40 / CARTOSAT-2F | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Anubnavthakur) | Cygnus NG-05 (OA-5) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Xiaoqing) | Cygnus NG-05 (OA-5) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Sokolsky) | Cygnus NG-05 (OA-5) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Wingo) | Cygnus NG-05 (OA-5) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Beccadewey) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Nate) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Bridgeman) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Drmuzz) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Cubecheese) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jeff) | Dragon CRS-6 (SpX-6) | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Nick-Allain) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Kane) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Theresacondor) | OA-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Chris) | PSLV-C30 / ASTROSAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jeroen) | PSLV-C30 / ASTROSAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Peter) | PSLV-C30 / ASTROSAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Joel) | PSLV-C30 / ASTROSAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Victor Andew) | PSLV-C45 / EMISAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Elham) | PSLV-C45 / EMISAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Beaudacious) | PSLV-C45 / EMISAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (JoranJoran) | PSLV-C45 / EMISAT | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Alex Maddy) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Yndrd) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (GregRobinson) LEO | - | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Morag) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (E. Jatta) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (DustInTheWind) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Lily Jo) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Wanli) | Meteor-M 2 №2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Theodosia) | PSLV-C48 / RISAT-2BR1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (JPG Squared) | PSLV-C48 / RISAT-2BR1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (HiMomAndDad) | PSLV-C48 / RISAT-2BR1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Pappy) | PSLV-C48 / RISAT-2BR1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Ursa Avion) | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Oscarlator) | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Squarejaws)LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Djuproera)LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Schmidtfall)LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (EthanOakes) LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (DaveHartzell)LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (FJMSRBijanka) LEO | Vega VV16 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (DayWzAGood)LEO | Gonets-M | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (nichol)LEO | Gonets-M | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Slicers)LEO | Gonets-M | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Susurrus)LEO | Gonets-M | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Svante-Amanda)LEO | Vega VV18 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Baxter-Olivier)LEO | Cygnus NG-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Diara)LEO | Cygnus NG-14 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-1 (Prototype)LEO | Dnepr / UniSat-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Chanusiak)LEO | ‘It’s-Business-Time’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Zupanski)LEO | ‘It’s-Business-Time’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Marshall)LEO | ‘Still-Testing’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Tallhamn)LEO | ‘Still-Testing’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mynameisjeff)LEO | Transporter-12 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Roundtripper)LEO | Transporter-12 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Alisia)LEO | Transporter-12 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Cael)LEO | ‘Four-Of-A-Kind’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Oba-Ni-Jesu)LEO | ‘Four-Of-A-Kind’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Valhalla)LEO | ‘Four-Of-A-Kind’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Nimbus 2000)LEO | ‘Four-Of-A-Kind’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mano)LEO | ‘Baby-Come-Back’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Deverill-M-T)LEO | ‘Baby-Come-Back’ | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (VanDenDries)LEO | Transporter-5 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (TennysonLily)LEO | Transporter-5 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mimi 1307)LEO | Transporter-5 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Karen B)LEO | Transporter-5 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Miriwari)LEO | Transporter-3 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Djirang)LEO | Transporter-3 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Forest-1 (LEMUR-2 Rohovithsa, OroraTech-1)LEO | Transporter-3 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (King-Julien)LEO | Transporter-3 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Ramonamae)LEO | Transporter-3 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jeremiah)LEO | PSLV-C49 / EOS-01 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Wallace)LEO | PSLV-C49 / EOS-01 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jindra)LEO | PSLV-C49 / EOS-01 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Ozarak)LEO | PSLV-C49 / EOS-01 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (SpecialK)LEO | Vega VV18 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (CarlSantaMari)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Merima)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (AC-Cubed)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Johnny-Treires)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (AnnaBanana)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jackson)LEO | Transporter-2 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mango1)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (SaoirSedh5Guo)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Ruairi-Eilidh)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (NoobNoob) | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Neva)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Nally Wacker)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Jennifer Song)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Chantal)LEO | Transporter-1 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| GNSS-4 (LEMUR-2 Romeo-n-Leo)LEO | Transporter-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| KAUST (LEMUR-2 OnReflection)LEO | Transporter-7 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Philari) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (MMolo) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Steve Albers) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Disclaimer) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (FuenteTaja-01) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Emmaculate) | Transporter-6 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Aadam-Aliyah) | Transporter-8 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Naziyah) | Transporter-8 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Forest-2 (LEMUR-2 Embrionovis) | Transporter-8 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (NanaZ) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mango2B) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Mango2A) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Vindlér-1.4 (SNC-4, LEMUR-2 Good Vibes) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Vindlér-1.3 (SNC-3, LEMUR-2 Sanita-Vetra) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Vindlér-1.2 (SNC-2 LEMUR-2 Dilightfull) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| Vindlér-1.1 (SNC-1, LEMUR-2 The Cleaner) | Transporter-9 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Ahmed-Asrar) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Squirrelcomm) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Marhisyam) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Lloyd) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Sierrini) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Stella) | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| Hubble-1 (LEMUR-2 Johnny Truong) | Transporter-10 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| Hubble-2 (LEMUR-2 Rocinante) | Transporter-10 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| Hubble-3 (LEMUR-2 Tomato Ketchup)LEO | Transporter-11 | Spire Global |  | Earth Observation |
| LEMUR-2 (Feldhus) | Transporter-10 | Spire Global |  | Communication |
| LEMUR-2 (Charlie-Rose) | Transporter-10 | Spire Global |  | Communication |